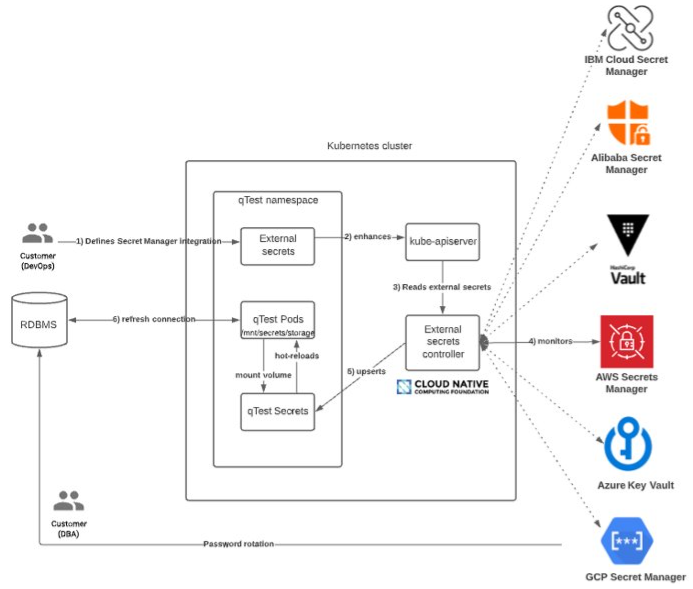
Kubernetes External Secrets with qTest
The containerization through Kubernetes allows you to integrate qTest with external secrets managers, such as AWS Secrets Manager. This enables support for password rotation and the storing of the qTest database password in an external secret manager. Changes are rapidly caught by qTest Manager.
The secret which contains the password the database should be named as qtest-manager-secret. To use SSL database connections, map the certificate as qtest-db-root-secret.
It works as follows:
-
The integration with external secret managers is accomplished via CustomResourceDefinitions (CRDs).
-
Changes to external secrets are upserted into Kubernetes Secrets, which is mounted as volume within the container.
-
qTest Manager hot-reloads the secret and refreshes DB connections .
-
Other qTest applications then use Stakater Reloader to reload secrets as a rolling update.
The diagram below offers an overview of this feature.
Configuration example for AWS Secrets Manager
The AWS Secrets Manager integration example below relies on the Kubernetes External Secrets framework.
apiVersion: "kubernetes-client.io/v1"
kind: ExternalSecret
metadata:
name: qtest-liquibase-secret
namespace: qtest
spec:
backendType: secretsManager
data:
- key: <AWS SECRET MANAGER KEY>
name: client.jdbc.postgres.password
property: password
---
apiVersion: "kubernetes-client.io/v1"
kind: ExternalSecret
metadata:
name: qtest-manager-secret
namespace: qtest
spec:
backendType: secretsManager
data:
- key: <AWS SECRET MANAGER KEY>
name: client.jdbc.postgres.password
property: password
- key: <AWS SECRET MANAGER KEY>
name: mail.password
property: password
- key: <AWS SECRET MANAGER KEY>
name: client.jdbc.postgres.readonly.password
property: password
- key: <AWS SECRET MANAGER KEY>
name: s3.secretKey
property: s3secretkey
- key: <AWS SECRET MANAGER KEY>
name: s3.accessKey
property: s3accesskey