Frameworks
By default, NeoLoad provides a simplified User Path, based partly on the detected framework and partly on the type of Push application.
AMF polling
After the recording, a User Path using AMF polling is displayed as follows.
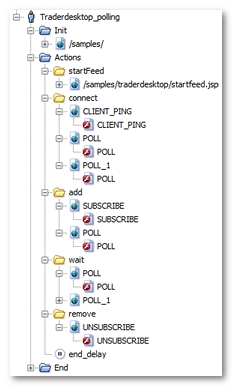
Note: AMF polling requests are identified as having a name with the POLL_XXX format.
Once processed by the NeoLoad Post-recording wizard, the User Path is modified as follows.
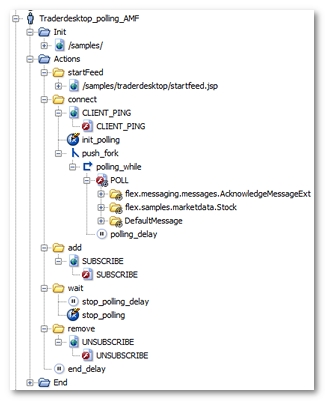
NeoLoad has made the following noticeable changes:
-
All the AMF polling requests have been grouped into a single polling request (
POLLfor example). This request has been placed in a loop (polling_whilefor example), which continues to loop until theNL-stopPollingvariable generated by NeoLoad becomestrue. Lastly, the loop itself has been placed in a secondary execution thread using a fork action (push_forkfor example). For more information, see Polling requests -
NeoLoad identifies the different types of message returned through the Push channel during recording. These different types of message are modelized by the Push messages (
flex.samples.marketdata.Stockorflex.messaging.messages.AcknowledgeMessageExtfor example). -
The variable modifier
init_pollinginitializes theNL-stopPollingvariable, with thefalsevalue, to have the polling function work on every Virtual User iteration. -
The
polling_delayis the average of the time intervals between two polling requests in the original User Path. -
The
stop_pollingvariable modifier triggers the exit from the polling loop by modifying the value of theNL-stopPollingvariable.
AMF streaming
After the recording, a User Path using AMF streaming is displayed as follows.
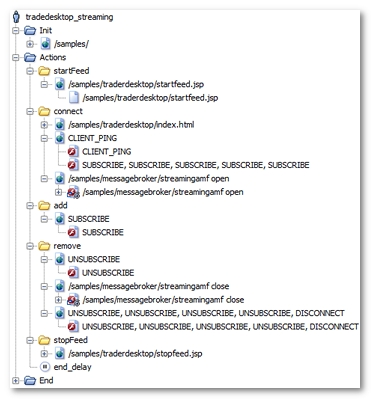
AMF streaming requests are identified as having a name with the <path> open and <path> close formats.
Once processed by the NeoLoad Post-recording wizard, the User Path is modified as follows.
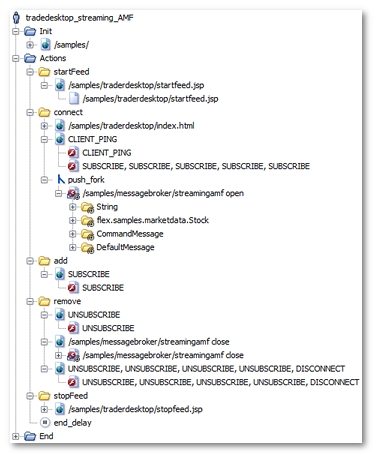
NeoLoad has made the following noticeable changes:
-
The open Push request (
/samples/messagebroker/streamingamf openfor example) has been placed in a secondary execution thread,push_fork. -
NeoLoad identifies the different types of message returned through the Push channel during recording. These different objects are modelized by the Push messages (
flex.samples.marketdata.StockorStringfor example). -
The close Push request (
/samples/messagebroker/streamingamfclose for example) tells the server to stop Push. Upon receiving the request, the server closes the streaming request/samples/messagebroker/streamingamf open, allowing NeoLoad to move on to the next action. There are no other actions in thepush_forkobject so the secondary thread ends.
RTMP streaming
To be able to record RTMP requests, the Adobe RTMP option must be checked in the recording window.
After the recording, a User Path using the RTMP protocol is displayed as follows.
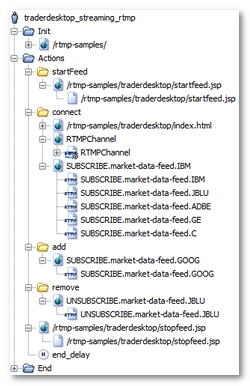
The RTMP Push channel is represented by the RTMPChannel object. Its recorded response contains all the messages sent by the server through the Push channel.
Once processed by the NeoLoad Post-recording wizard, the User Path is modified as follows.
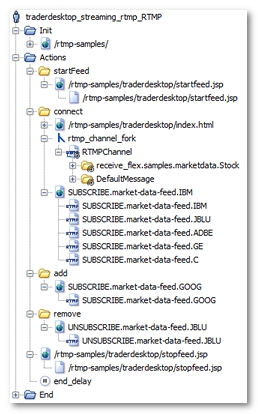
NeoLoad has made the following noticeable changes:
-
The request representing the Push channel (
RTMP_Channelfor example) has been placed in a secondary execution thread (rtmp_channel_fork). -
NeoLoad identifies the different types of message returned through the Push channel during recording. These different types of message are modelized by the Push messages (
receive_flex.samples.marketdata.Stockfor example here).
RTMPT streaming/polling
At the end of recording, launch a dynamic parameter search for NeoLoad to be able to handle the RTMP dynamic session IDs.
After the recording, a User Path using the RTMPT protocol is displayed as follows:
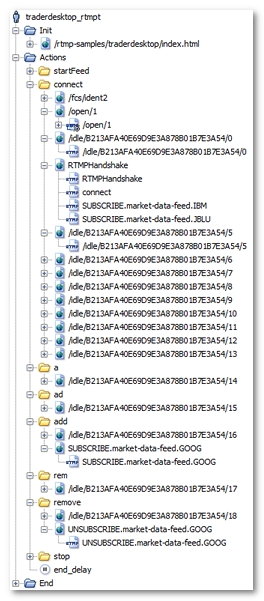
The following points should be noted:
-
A large number of HTTP requests with the /idle/ prefix have been recorded. These requests are polling requests.
-
When a Container is added during entering, polling requests also are added. This explains the a, ad, and rem. Containers.
Once processed by the Post-recording wizard, the User Path is modified as follows:
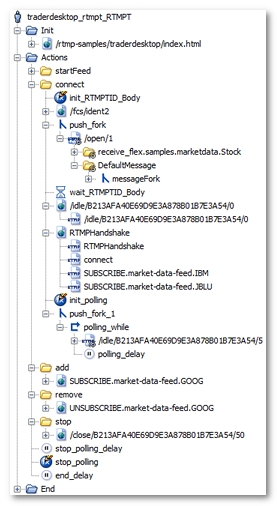
NeoLoad has made the following noticeable changes:
-
The request representing the opening of the RTMPT session (
/open/1for example) has been placed in a secondary execution thread (push_fork) since it is a blocked process. A Variable Extractor (RTMPTIDfor example) has been configured to extract and re-inject the RTMPT session variable in each of the following requests:/idle/XXX,/send/XXXor/close/XXX. Execution of the main thread is put on hold until the RTMPTID session variable is retrieved, using thewait_RTMPTID_Bodyobject. -
The variable modifier
init_RTMPTID_Bodyresets theRTMPTID_Bodyvariable, and the waiting time for a new value is considered on every Virtual User iteration. -
All the RTMPT polling requests (except the first one) are grouped into a single polling request (
/idle/${RTMPTID}/5for example), reducing the number of requests considerably. If a Container becomes empty (a, ad, and rem for example), it is automatically deleted. For more information, see Polling requests. -
The variable modifier
init_pollinginitializes theNL-stopPollingvariable, with thefalsevalue, to have the polling function work on every Virtual User iteration. -
The request representing the RTMPT Push channel (
/idle/${RTMPTID}/5for example) has been placed in a loop (polling_while), which continues to loop until theNL-stopPollingvariable generated by NeoLoad becomes true. Lastly, the loop itself has been placed in a secondary execution thread using a fork action (push_fork_1for example). -
NeoLoad identifies the different types of message returned through the Push channel during recording. These different types of message are modelized by the Push messages (
receive_flex.samples.marketdata.Stockfor example). -
The
polling_delaypolling delay is the average of the time intervals between two polling requests in the original User Path. -
The
stop_pollingvariable modifier stops the polling loop by modifying the value of theNL-stopPollingvariable.
ICEfaces polling
NeoLoad supports the open-source ICEfaces server and its commercial version, ICEfaces EE.
Versions 1.8.2a onwards of the ICEfaces server also feature an API that allows making use of the Push messages generated by the server itself as well as their associated timestamps. To be able to use the NeoLoad Push messages, the names of the ICEfaces beans and the beans associated timestamps must be published in the ICEfaces application.
The tested ICEfaces application is modified:
Modifying the ICEfaces bean:
The Java file containing the ICEfaces bean must contain a method publishing the additional information. For example, the MyBean.java file might contain the following code:
public class MyBean implements Renderable {
...
private GroupAsyncRenderer mybean;
private String renderInfo;
...
public String getRenderInfo()
{
String currentRenderInfo = mybean.getLastRenderInfo();
if(!currentRenderInfo.equals(renderInfo))
{
renderInfo = currentRenderInfo;
return currentRenderInfo;
} else {
return "";
}
}
...
Modifying the .jspx file:
The .jspx file containing the visual part of the content rendered in the browser must send back this information in the page. One idea is to send back the information in a hidden layer.
The code might take the following form:
...
<div id="hiddenDiv">
...
<ice:outputText value="MyBean #{MyBean.renderInfo}"/>
...
</div>
...After the recording, a User Path using the ICEfaces Push Framework is displayed as follows.
Note: At the end of recording, a dynamic parameter search must be launched for NeoLoad to be able to handle the ICEfaces dynamic session IDs and the JSF ViewState.
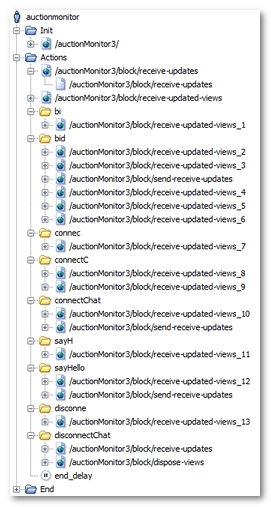
The following points should be noted:
-
The ICEfaces polling is divided into two request categories: requests to the
/receive-updated-viewsservlet and those to the /receive-updates servlet. This explains the large number of this type of requests. -
User clicks are represented by requests to the
/send-receive-updatesservlet. -
When a Container is added during entering, polling requests also are added. This explains the
bi, connec...Containers.
Once processed by the NeoLoad Post-recording wizard, the User Path is modified as follows.
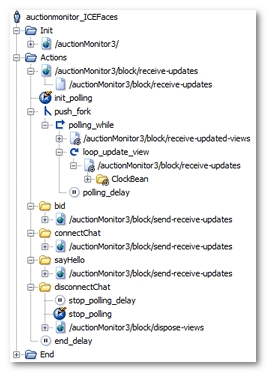
NeoLoad has made the following noticeable changes:
-
The two categories of polling requests have been grouped together: requests with the form
XXX/receive-updated-viewson the one hand and those with the formXXX/receive-updateson the other hand. This reduces the number of requests considerably. If a Container becomes empty (as is the case with bi and connec here for example), it is automatically deleted. For more information, see Polling requests -
The Variable Extractor
viewsToUpdatehas been placed on the first polling request (/auctionMonitor3/block/receive-updated-viewsfor example), which retrieves the id's for the ICEfaces views to be updated. This is why the second polling request has been placed in a loop (loop_update_viewfor example), in order to issue an update request for each previously-extracted view. -
The request representing the ICEfaces Push channel (
/auctionMonitor3/block/receive-updatesfor example) has been placed in a loop (polling_while), which continues to loop until the NL-stopPolling variable generated by NeoLoad becomes true. Lastly, the loop itself has been placed in a secondary execution thread using a fork action (push_forkfor example). -
NeoLoad identifies the different types of message returned through the Push channel during recording, provided that the server being tested is version 1.8.2a or upwards and that the developers have published the required additional information. These different types of message are modelized by the Push messages (ClockBean for example).
-
The
polling_delaypolling delay is the average of the time intervals between two polling requests in the original User Path. -
The variable modifier
init_pollinginitializes theNL-stopPollingvariable, with thefalsevalue, to have the polling function work on every Virtual User iteration. -
The
stop_pollingvariable modifier stops the polling loop by modifying the value of theNL-stopPollingvariable.
Lightstreamer polling
At the end of recording, a dynamic parameter search must be launched for NeoLoad to be able to handle the Lightstreamer dynamic session IDs.
After the record, a User Path using polling with the Lightstreamer Framework is displayed as follows.
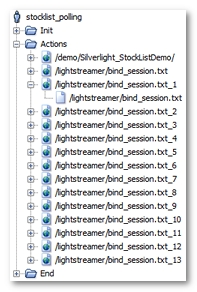
The following point should be noted:
-
A large number of HTTP requests with the format
XXX/bind_session.jshave been recorded. These requests are polling requests.
Once processed by the Post-recording wizard, the User Path is modified as follows.
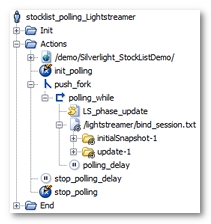
NeoLoad has made the following noticeable changes:
-
All the Lightstreamer polling requests have been grouped into a single polling request (/lightstreamer/bind_session.js for example). This request has been placed in a loop (
polling_whilefor example), which continues to loop until the NL-stopPolling variable generated by NeoLoad becomes true. Lastly, the loop itself has been placed in a secondary execution thread using a fork action (push_fork for example). For more information, see Polling requests. -
The variable modifier
init_pollinginitializes theNL-stopPollingvariable, with the false value, to have the polling function work on every Virtual User iteration. -
NeoLoad identifies the different types of message returned through the Push channel during recording. These different types of message are modelized by the Push messages (
initialSnapshot-1orupdate-1for example). -
For each response returned by the Push channel, NeoLoad cuts up the JavaScript call into messages. NeoLoad recognizes three types of Lightstreamer call by default:
initialSnapshot-X,update-Xandheartbeat, where X represents the updated HTML component. -
The Lightstreamer
LS_phaseparameter is handled using theLS_phaseVariable Extractor set both on the session creation request (creation_session.jsfor example) and on the Push request (/lightstreamer/bind_session.txtfor example). A JavaScript action (LS_phase_update1for example) increments the value of theLS_phasevariable at each loop iteration to reproduce the browser behavior. -
The
polling_delaypolling delay is the average of the time intervals between two polling requests in the original User Path. -
The
stop_pollingvariable modifier stops the polling loop by modifying the value of theNL-stopPollingvariable.
Lightstreamer streaming
At the end of recording, a dynamic parameter search must be launched for NeoLoad to be able to handle the Lightstreamer dynamic session IDs.
After the recording, a User Path using streaming with the Lightstreamer framework is displayed as follows.
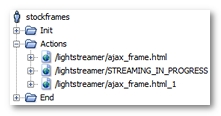
The Lightstreamer streaming request is easily identified, since it ends with the path /STREAMING_IN_PROGRESS.
Once processed by the Post-recording wizard, the User Path is modified as follows.
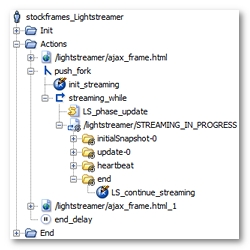
NeoLoad has made the following noticeable changes:
-
The request representing the Lightstreamer Push channel (
/lightstreamer/STREAMING_IN_PROGRESSfor example) has been placed in a loop (streaming_whilefor example), which continues to loop until theLS_end_streamingvariable generated by NeoLoad becomestrue(the streaming request can be executed several time if the length of the response is over 300 Kb). Lastly, the loop itself has been placed in a secondary execution thread using a fork action (push_forkfor example). -
The variable modifier
init_streaminginitializes theLS_end_streamingvariable, with thefalsevalue, to have the streaming function work on every Virtual User iteration. -
NeoLoad identifies the different types of message returned through the Push channel during recording. These different types of message are modelized by the Push messages (
initialSnapshot-0orupdate-0for example). The end message is added to the streaming request to handle several executions of the streaming request (if the response length is over 300 Kb). -
For each response returned by the Push channel, NeoLoad cuts up the JavaScript call into messages. NeoLoad recognizes three types of Lightstreamer call by default:
initialSnapshot-X,update-Xandheartbeat, where X represents the updated HTML component. -
The Lightstreamer
LS_phaseparameter is handled using theLS_phaseVariable Extractor set on the session creation request (creation_session.jsfor example). A JavaScript action (LS_phase_updatefor example) increments the value of theLS_phasevariable to reproduce the browser behavior. Lastly, this variable is used in the open streaming request (/lightstreamer/STREAMING_IN_PROGRESSfor example).
WebSync polling
At the end of recording, a dynamic parameter search must be launched for NeoLoad to be able to handle the WebSync dynamic session id's (clientId).
After the recording, a User Path using the WebSync Push Framework is displayed as follows.
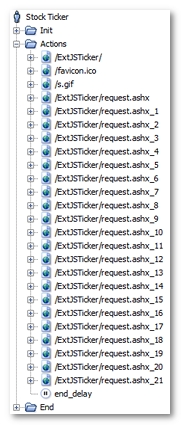
The following point should be noted:
-
A large number of HTTP requests with the format
XXX/request.ashxhave been recorded. These requests are polling requests.
Once processed by the Post-recording wizard, the User Path is modified as follows.
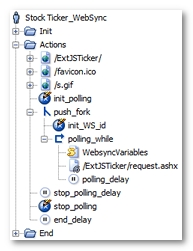
NeoLoad has made the following noticeable changes:
-
All WebSync polling requests have been grouped into a single polling request (
/request.ashxfor example). This request has been placed in a loop (polling_whilefor example), which continues to loop until the NL-stopPolling variable generated by NeoLoad becomestrue. Lastly, the loop itself has been placed in a secondary execution thread using a fork action (push_forkfor example). For more information, see Polling requests. -
The variable modifier
init_pollinginitializes theNL-stopPollingvariable, with thefalsevalue, to have the polling function work on every Virtual User iteration. -
The WebSync
idparameter is handled using a JavaScript action (WebsyncVariablesfor example). At the first polling loop, the initial value is calculated in relation to the request that precedes the polling; it is then increment at each loop iteration to reproduce the browser behavior. -
The variable modifier
init_WS_idresets theWS_idvariable to make the WebSync parameter consistent on every Virtual User iteration. -
The
polling_delaypolling delay is the average of the time intervals between two polling requests in the original User Path. -
The
stop_pollingvariable modifier stops the polling loop by modifying the value of theNL-stopPollingvariable.
Siebel polling
Siebel applications have a real-time message broadcasting feature that can send specific information to certain users in particular. The information usually is displayed at the bottom of the application screen as scrolling text; this is known as the message bar. Each client connected to the Siebel application sends a polling request at regular intervals to update the message bar settings and content.
After the recording, a User Path using polling to update the message bar is displayed as follows.
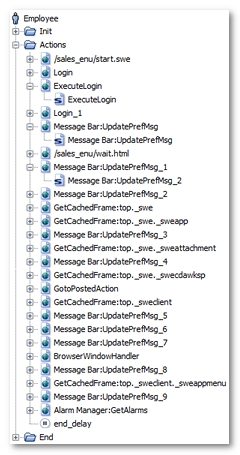
Note: When recording a scenario, NeoLoad identifies these requests as having a name with the form Message Bar:UpdatePrefMsg_XXX.
Once processed by the Post-recording wizard, the User Path is modified as follows.
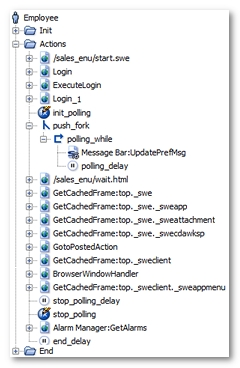
NeoLoad has made the following noticeable changes:
-
All the Siebel polling requests to update the message bar have been grouped into a single polling request (
Message Bar:UpdatePrefMsgfor example). This request has been placed in a loop (polling_whilefor example), which continues to loop until theNL-stopPollingvariable generated by NeoLoad becomes true. Lastly, the loop itself has been placed in a secondary execution thread using a fork action (push_forkfor example). For more information, see Polling requests -
The variable modifier
init_pollinginitializes theNL-stopPollingvariable, with thefalsevalue, to have the polling function work on every Virtual User iteration. -
The
polling_delaypolling delay is the average of the time intervals between two polling requests in the original User Path. -
The
stop_pollingvariable modifier stops the polling loop by modifying the value of theNL-stopPollingvariable.
HTML5 Server-Sent Events
Server-Sent Events are a technology for providing push notifications from a server to a browser in the form of DOM (Document Object Model) events. The Server-Sent Events EventSource API is standardized as part of HTML5.
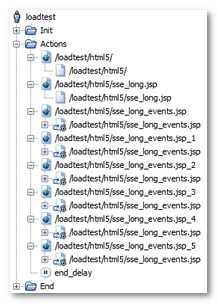
After the recording, a User Path with the HTML5 Server-Sent Events (SSE) technology is displayed as follows.
Once processed by the Post-recording wizard, the User Path is modified as follows.
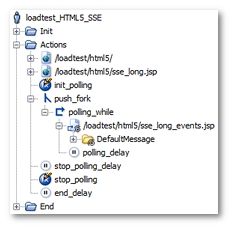
NeoLoad brings the following changes:
-
All the requests generating events are collected in a single request, for example
/loadtest/html5/sse_long_events.jsp. The request is included in a while action, for examplepolling_while, which iterates until theNL-stopPollingvariable generated by NeoLoad switches to true. Also, the while action is itself in a secondary execution thread with the fork action, for examplepush_fork. For more information, see Polling requests. -
The variable modifier
init_pollinginitializes theNL-stopPollingvariable, with thefalsevalue, to have the polling function work on every Virtual User iteration. -
The
polling_delaypolling delay is extracted from the polling response. When the server sends a reconnection order, the variable is extracted. Otherwise, the default value is 3 seconds. The delay simulates the timeout between two requests. -
The
stop_pollingvariable modifier makes it possible to stop the polling loop by changing the value of theNL-stopPollingvariable