Follow a link from the previous request
This tutorial looks at the case where the request type Follow a link from the previous request is used. This is one of the methods provided by NeoLoad for extracting data from an HTML page returned by the server. For more information about the various methods of extracting data, see Choose a data extraction method.
This extraction method can be used when a request is the result of a standard HTML link of the type <a href=""...>. The aim is to play back a link and its parameters as returned by the server during the test instead of playing back the recorded link. This tutorial will show you two ways of telling NeoLoad how to follow the link: either to search for an attribute containing a specific value, or to search for one or more values in the link parameters.
The tutorial describes one of the steps in the methodology relating to designing a Virtual User. For an overview of designing a Virtual User, see Design process.
Understand the problem
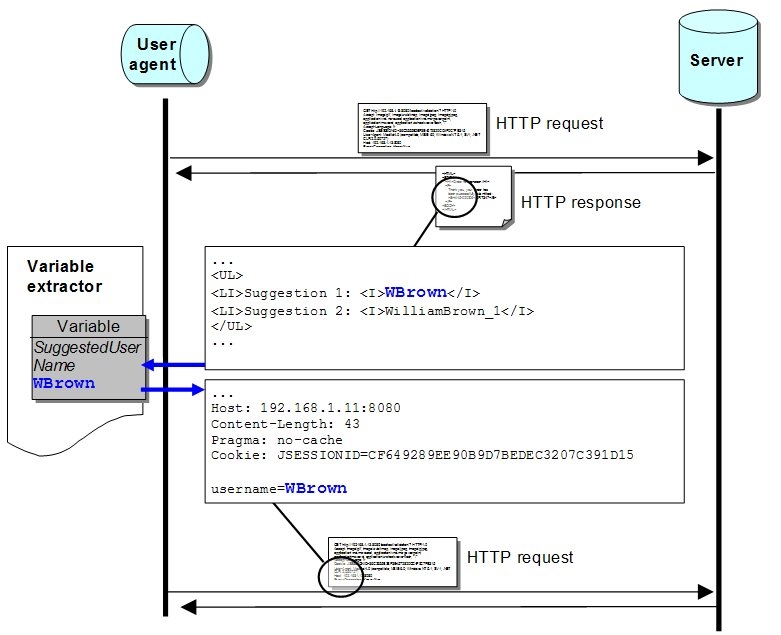
An HTML page often contains dynamic elements generated by your application. Typical examples of such dynamic elements are request parameters used to determine a context, a search context for instance. The following code is an extract from an HTTP response containing such dynamic elements.
<HTML>
<BODY>
...
<A href="index.jsp?searchID=24257622&page=2">Next Page</A>
</BODY>
</HTML>The HTML page displays a link called Next Page that refers to the index.jsp page with two dynamic parameters: searchID and page. If this link is followed during the recording phase and replayed in a scenario, NeoLoad will use the recorded values. This is definitely not the desired behavior and this tutorial mainly addresses this issue.
To deal with dynamic URLs, NeoLoad provides a mechanism that automatically finds a URL in the previous HTTP response and injects it in the following HTTP request.
Ensure this tutorial applies to your case
For the purposes of this tutorial, a scenario has been recorded, in which you can start on a search page, enter your search criteria, and browse the results going from one page to the next. The following illustration shows a very simple page of results. The search criteria have been entered beforehand and the user is browsing the results from page to page:

The following screenshot shows the content of the HTTP response for this HTML page. As explained previously, it contains a link that refers to the page index.jsp, with two dynamic parameters: searchID and page.
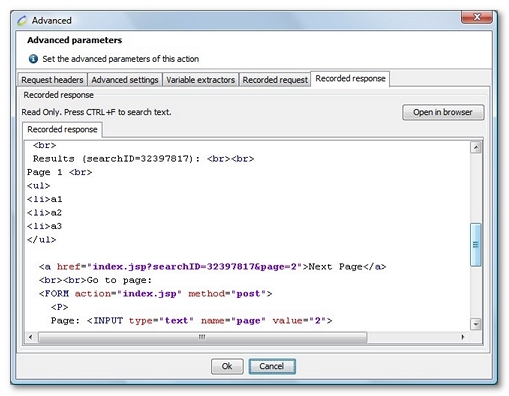
You might obtain this screenshot by selecting the page containing the Next page link. You might then select the HTTP request, click on the Advanced button and select the Recorded response tab.
This tutorial will show you several ways of telling NeoLoad how to find and follow the HTML link Next Page.
Follow the link
This section shows different ways to follow links:
-
How to follow a link using attribute value.
-
How to follow a link using the definition.
The following procedure describes how to find the link identified by the text Next Page in the response referred to earlier. It will also allow you to dynamically play back all the link parameters values during playback.
To follow a link using an attribute value, follow these steps:
-
Select the HTTP request containing the URL with dynamic parameters:
-
Select the Design section.
-
Select the Virtual Users tab.
-
Open out the corresponding Virtual User and HTML page.
-
Select the HTTP request containing the dynamic URL; this request belongs to the HTML page that that follows the page containing the HTTP request described earlier.
-
During the recording phases, NeoLoad identifies the URL parameters that will be sent when the link is followed. In the example, these parameters are
searchIDandpage.
-
-
Change the HTTP request type. In the Type drop-down list, change the HTTP request type from Manually define the request to Follow a link from the previous request.
-
Make sure the referrer is the preceding request. In the Extract and follow a link from field, make sure that the request shown is the one containing the
hrefHTML tag. If this is not the case, click on the Change the referrer button and select the correct referrer. -
Select the link attribute. Click on the Link whose option box, then select the attribute to search for. For the example, select link text to tell NeoLoad to search for a link content of the type
<a href=..>[content_to_be_searched_for]</a> -
Enter the attributes value. In the is field, enter the attribute value to search for, in this case "Next Page". This tells NeoLoad to search for a link whose form is:
<a href=..>Next Page</a>.This will instruct NeoLoad to extract any link whose label is "Next Page" and dynamically inject it during the test.
The following procedure describes how to find the link defined by the searchID and page parameters in the previous response. It will also allow you to dynamically play back the searchID value during playback.
To follow a link using the definition, follow these steps:
-
Select the HTTP request containing the URL with dynamic parameters:
-
Click on the Advanced button to go into the Design section.
-
Select the Virtual Users tab.
-
Open out the corresponding Virtual User and HTML page.
-
Select the HTTP request containing the dynamic URL; this request belongs to the HTML page that follows the page containing the HTTP request described earlier.
-
During the recording phases, NeoLoad identifies the URL parameters that will be sent when the link is followed. In the example, these parameters are
searchIDandpage.
-
-
Change the HTTP request type. In the Type drop-down list, change the HTTP request type from Manually define the request to Follow a link from the previous request.
-
Make sure the referrer is the preceding request. In the Extract and follow a link from field, make sure that the request shown is the one containing the
hrefHTML tag. If this is not the case, click on the Change the referrer button and select the correct referrer. -
Enter the link definition. Make sure that the
ServerandPathcombination points to the link in question. Here, you are telling NeoLoad to search for a link whose URL points to the selected server and specified path, such as<a href="http://jack:9090/loadtest/simple-search/index.jsp"..>..</a> -
Select the attributes to be dynamically extracted.
-
In the Request Parameters section, double-click on the attribute to be dynamically extracted from the server response, in this case
searchID. Next, click on the option box The parameter must be present, whatever its value. -
Here, you are telling NeoLoad to refine its search for the link , such as
<a href="http://jack:9090/loadtest/simple-search/index.jsp?page=2&searchID=.."..>..</a> -
This will instruct NeoLoad to extract any link whose URL starts with
http://<jack>/loadtest/simple-search/index.jsp, whosepageattribute is "2" and having asearchIDattribute (whatever its value), and dynamically inject it during the test. -
For the dynamic path value, the
Pathexpression,/loadtest/simple-search/index.jspin the example, also may be dynamic, its value being generated by your application each time the link is requested. In this case, you must tell NeoLoad to extract the value from the response and re-inject it before requesting the URL. If the link path is dynamic, click Regular expression and use the appropriate regular expression to indicate which path to extract. This may simply be.*if there are no other links with the same parameters.
For the dynamic server value, theServerused by the request may also be dynamically generated by your application. In this case you must create a server manually, configuring the server host name with a regular expression that matches the server name. Then, you must set the server for this request to the server you have just created.
-