Validation
Allows adding assertions to the server responses to check their validity. The validity of the content returned by the server may be checked using the following criteria: delay, page size or page content.
Note: Validation cannot be applied to failed requests (HTTP error, network error, and so on).
Duration
Specifies the maximum delay tolerated in ms.
Content Length
Defines the exact, minimum and maximum sizes of the server response body. HTTP header lengths are disregarded. The default length is the length of the server response content at the time of recording. Greater than denotes greater than or equal to; Lower than denotes smaller than or equal to.
Response Content
Checks whether or not the server response contains a certain content. The server response is considered valid if all the content conditions are satisfied.
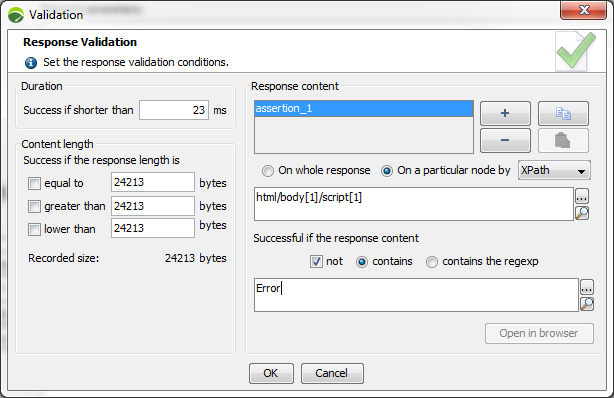
Depending on the type of HTTP response, the validation can be based:
-
On whole response: The validation check will be carried out on the HTTP responses headers and body. This is the default option.
-
On a particular node: The validation check will be carried out on one of the nodes in the response body. This node is defined using XPath or JSONPath expressions. This option is available for XML and JSON responses, which includes HTML, XHTML, SOAP, GWT, Adobe Flex/AMF, Oracle Forms, Java Serialization, RTMP, Siebel responses, etc. A click on the facing list box allows selecting the required format.
Conditions available are:
-
contains: Checks if the body of the server response contains the specified text (example:
<span class="welcome">Welcome</span>). -
contains regular expression: Checks if the body of the server response contains the specified regular expression (example:
<span class="welcome">Welcome \w+ \w+ </span>).
Note that the content assertion may contain variables.
For more information, see Regular expressions.
Validate a JSON response
Validating a response in JSON format is almost identical to the standard procedure. For more information about validating a HTTP request, see Global validation.
You may define validations on the JSON response using JSONPath. To recap, JSONPath is a syntax that points to a portion of a JSON document.
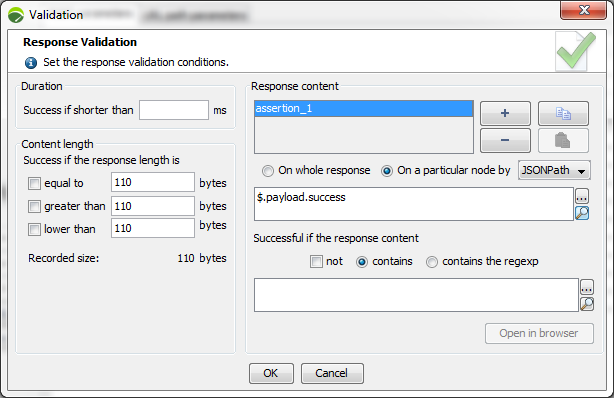
For a JSON request, response validators may be created:
-
For the entire response: These are standard validators that validate the response content.
-
For a particular JSON node: These are validators that are specific to the JSON modules. A JSON node can then be specified by selecting it in the dialog box that is displayed by clicking on the magnifying glass next to the field.
This will create a JSONPath expression based on the selected JSON node. You may edit the expression manually, but you must make sure the JSONPath expression remains valid. The JSONPath expression may be variabilized.
You will then return to the normal procedure, except that instead of carrying out the validation on the entire server response, it will be done only on the part specified by the JSONPath expression.
To create a response validator using JSONPath, follow these steps:
-
Create a validator.
-
Select the On a particular node by option and select JSONPath in the list box.
-
Click on the magnifying glass next to the text field below and select the JSON node to be validated.
-
Click OK.
The JSONPath expression for the selected node is displayed in the text field.
-
Select the text to be validated by clicking on the magnifying glass next to the text field below.
Note: Response validations on JSON nodes are resource-consuming operations. Only use this type of validation if absolutely necessary.
Validate an XML response
Validating a response in XML format is almost identical to the standard procedure. For more information about validating an HTTP request, see Global validation.
You may define validations on the XML response using XPath. To recap, XPath is a syntax that points to a portion of an XML document.
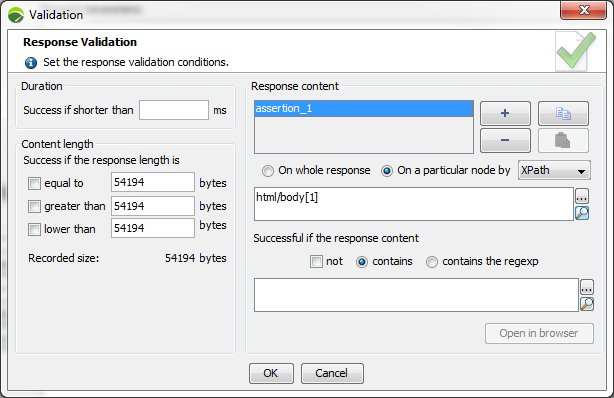
For an XML request, response validators may be created:
-
For the entire response: these are standard validators that validate the response content.
-
For a particular XML node: these are validators that are specific to the XML modules. An XML node can then be specified by selecting it in the dialog box that is displayed by clicking on the magnifying glass next to the field.
This will create an XPath expression based on the selected XML node. You may edit the expression manually, but you must make sure the XPath expression remains valid. The XPath expression may be variabilized.
You will then return to the normal procedure, except that instead of carrying out the validation on the entire server response, it will be done only on the part specified by the XPath expression.
To create a response validator using XPath, follow these steps:
-
Create a validator.
-
Select the On a particular node by option and choose XPath in the list box.
-
Click on the magnifying glass next to the text field below and select the XML node to be validated.
-
Click OK. The XPath expression for the selected node is displayed in the text field.
-
Select the text to be validated by clicking on the magnifying glass next to the text field below.
Note: Response validations on XML nodes are resource-consuming operations. Only use this type of validation if absolutely necessary.
Global validation
Allows adding content assertions for all the responses to all the requests in a User Path or Container. This answers the problem of needing common application validation rules for a number of requests within a same parent node.
To decide whether or not a response to a played request should be validated, NeoLoad retrieves the Content-Type header in the server response and checks if the header value appears in the list of types checked. By default, only responses with a text/html or text/xhtml Content-Type are checked. To edit the list of types to be checked, follow the Set application rules link. For more information, see Global validation. If the response type is listed, NeoLoad makes sure that the response content matches the various assertions.
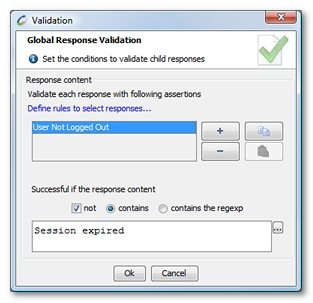
Note: Global validation is not applied to failed requests (HTTP error, network error...), nor to requests with responses in cache (304 HTTP status code).
Note: Using global validation uses a lot of memory so it is therefore recommended to use it sparingly and avoid applying it to large responses.
Global validation checks to see if a response contains, or does not contain, a certain content. The response is deemed valid if all the content conditions have been fulfilled.
The available condition types are:
-
contains: checks to see if the response body contains the specified text (for example
<span class="welcome">Welcome</span>). -
contains the regular expression: check to see if the response body matches the specified regular expression (for example
span class="welcome">Welcome \w+ \w+ </span>).Note that the content assertion may use NeoLoad variables.
For more information, see Regular expressions.