Shared queues
Shared queues are variables that enable dynamic content to be shared among Virtual Users. They follow the Producer-Consumer concept. They are used just like a NeoLoad variable and may be combined with other variables or static content (e.g.: product${SharedQueueVariable0}).
About shared queues
When a scenario is played out, it can be useful to have Virtual Users share extracted content. To do this, you need to use shared queues. A shared queue can be accessed by all Virtual Users and is used as a dynamic storage and exchange facility between Virtual Users. When a Virtual User adds a value to the store, it is placed at the end of the queue. The value remains there until another user requests it or, failing that, until the end of the test. When a value is requested, the oldest value in the queue is consumed and given to the requesting Virtual User.
A shared queue behaves like a First In, First Out (FIFO) pile, combined with the following limiting case policies:
-
If the queue is full, all new arrivals are lost.
-
If the queue is empty, the requesting Virtual User has to wait until a new arrival is added to the queue.
Create a shared queue
To enable interaction with a shared queue, it is necessary to use:
-
the Variable Modifier logical action, described in Variable modifier
-
the VariableManager JavaScript API, described in Class VariableManager
Open the variable editing window from the Edit > Variables menu, and click New Variable.
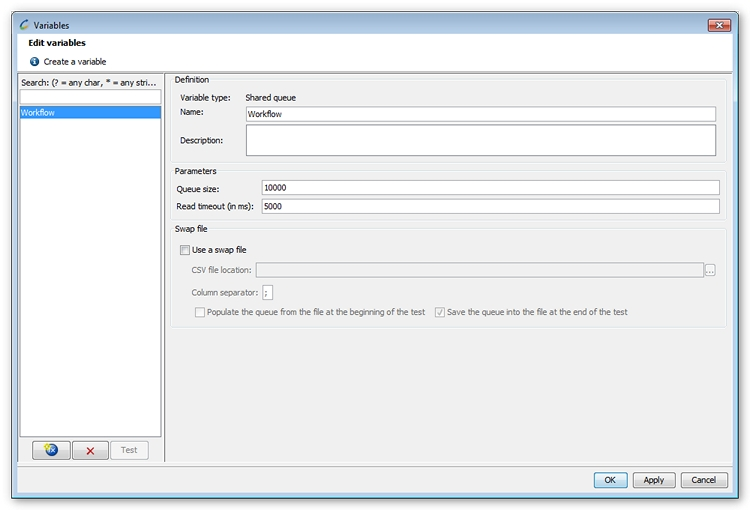
Select Shared queue as the variable type.
The variable parameters are:
-
Queue size: The maximum number of values the shared queue can contain.
-
Read timeout (in ms): The maximum wait time for a value (in milliseconds) if the queue is empty. This wait time only applies if no values are available in the queue. If this wait time is exceeded, the value ${sharedQueueName} is returned.
-
Use a swap file: A swap file may be used to pre-populate the queue at the start of the test or to save it at the end. To do this, check the Use a swap file box.
-
CSV file location: Location of the swap file. This file must be in .csv format with no headers and one column.
-
Column separator: The column separator used in the CSV file.
-
Three swap file use policies are available:
-
Read mode: Check the Populate queue from the file at the start of the test box.
-
Write mode: Check the Save queue to the file at the end of the test box.
-
Read and write mode: Check both boxes.
Add a value
Using the
Variable Modifierlogical action: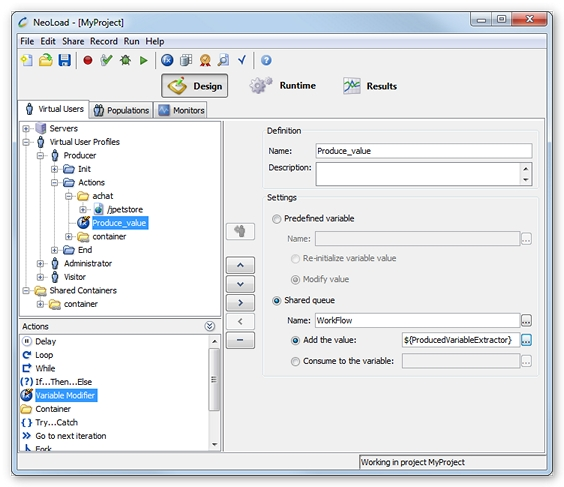
Select the Shared queue variable type.
-
Name: The name of the shared queue to which the value is to be added.
-
Add value: The expression containing the value to be added; the syntax is
${variableName}, but it also can be associated with static content (e.g.product_${productID})
The expression value is then added to the end of the queue. However, if the queue has reached its maximum capacity, the value will be lost.
-
Consume a value
Using the Variable Modifier logical action:
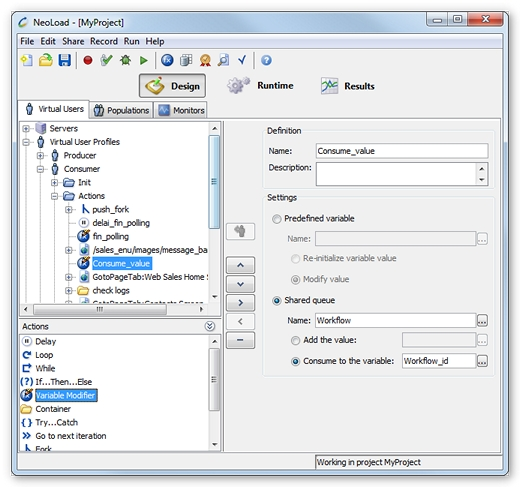
Select the Shared queue variable type
-
Name: The name of the shared queue from which the value is to be consumed.
-
Consume to variable: The variable to which the value in the queue is copied; the syntax is
variableName, omitting${}
The first available value will be extracted from the queue and assigned to the variable. If the queue is empty however, the Virtual User will wait for an available value until the timeout set when the queue was created. Once this has timed out, the value used is ${queueName}.
Consuming a variable can be done whenever the variable picker is available.