HTTP requests
In NeoLoad, an HTTP request is a request sent over a network using the HTTP or HTTPS protocol. Normally the request is followed by a server response, which can be in the form of an HTML web page, image or CSS file among others.
Create an HTTP request
This section describes how to create an HTTP request. To record a request using an existing client, refer to the Record a test scenario
To create an HTTP request in a User Path, follow these steps:
-
In the User Paths node, right-click on a Container (Transaction, page, etc.) and in the context menu, select Insert after > HTTP Request.
-
In the HTTP Request screen, you can choose between:
-
Empty: This will create a GET-type request to an existing server or will create a server if none was defined in the project.
-
From content: In this case, you can specify the content of request and response. You can paste your content that may be retrieved from a third-party tool (for example SoapUI, Postman, Fiddler, etc.).
Request: This will create both a request with the methods, the headers and the parameters defined in the content and a server if necessary. Otherwise, it will use the server defined in the pasted content.
Response: This will create a recorded response. This optional content may help define the type of response expected from the request. The content stands for an example of response to the request.
Providing a response content type is helpful for:
-
Using more easily Variable extractors. For more information, see Variable extractors
-
Testing your request in a more efficient way.
-
Comparing the content of the recorded response with the Check User Path one. For more information, see Check a user path
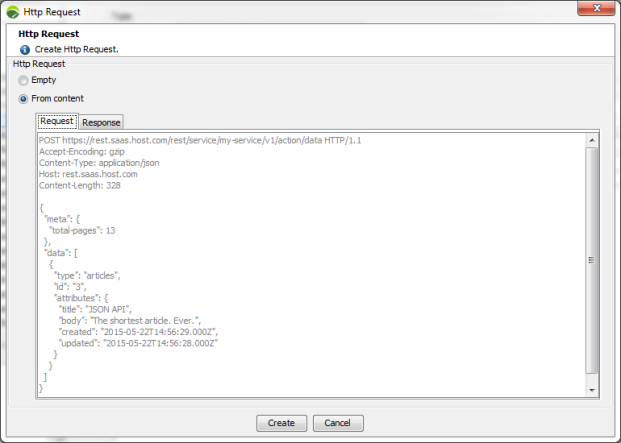
Note: It is mandatory to leave a blank line between the last header and the content.
Note: The content of the request is evaluated with the default charset of the operating system. If the request contains characters that are not included in that charset, you can specify a specific charset in the HTTP request header: Content-Type: application/text; charset=utf-8.
Type
There are 4 ways to define a request type:
-
Use a manual definition. Manually define the request. Allows entering the URL and set the parameters to be used for the request. For more information, see Use a manual definition
-
Follow a redirect of the previous request. Indicates that the present request is the target of an HTTP redirect in the response to the preceding request.
-
Follow a link from the previous request. Extracts and follows a link matching a dynamic definition. This option is useful when a scenario includes a click on a dynamically-generated link. The link is dynamically extracted from the results of the preceding request (referrer) and follows the link. For more information, see Follow a link from the previous request.
-
Submit a form from the previous request. Extracts and submits a form from a form in the previous request. This option is useful when a scenario includes the submission of a form containing a dynamic hidden field. The form is dynamically extracted from the results of the preceding request (referrer), allowing the dynamically-extracted values to be submitted. For more information, see Submit a form from the previous request