Create a User Path based on API requests
NeoLoad makes it possible to quickly design a test scenario to load test a Swagger API. The Import OpenAPI command allows importing all the requests of a Swagger API in NeoLoad to automatically include them in a new User Path.
Note: NeoLoad is compatible with Swagger 2 and Open API 3.
The Import OpenAPI command is accessible:
-
In the User Paths tab, with a right-click on the User Paths item in the tree view and by selecting Create a User Path > Import OpenAPI.
-
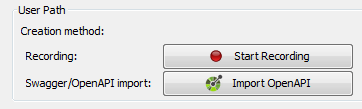
With a click on the Import OpenAPI button in the User Paths groups box.
-
With a click on the New User Path button.

The Import OpenAPI dialog box pops up to start the import configuration:
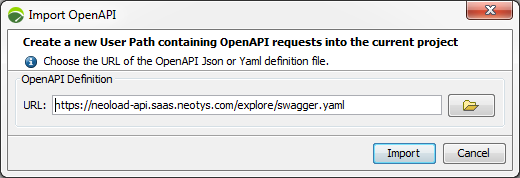
URL: The field must be filled in with the URL to the JSON or YAML file including the requests to import. A click on the folder icon allows selecting a file on a local machine.
A click on the Import button imports the requests and creates a User Path with the name of the API the requests have been imported from.
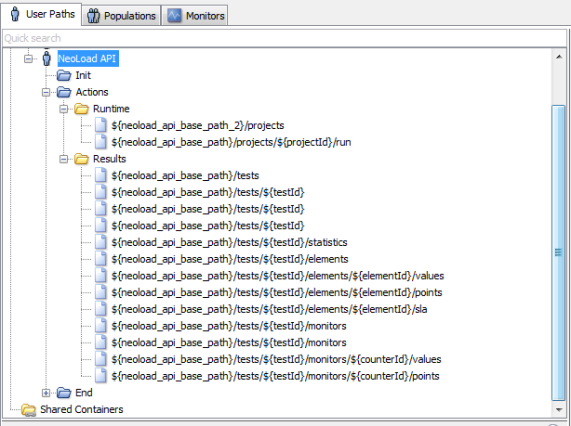
Also, in the design tree view, one or several (depending on the API structure) servers are created under the Servers node.
Requests and variables
The imported requests are named with the parameters they include. A click on a request allows configuring it as described in Requests
When an API method includes mandatory parameters, they are turned into variables in the request path. These variables are prefixed with the name of the imported API.
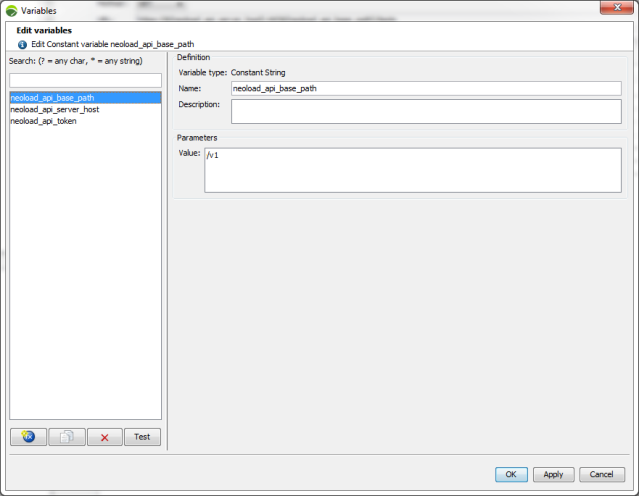
Also, during the import phase, two variables are automatically created:
-
<API name>basepath: The request base path.
-
<API name>serverhost: The server address.
Note: If the imported API requires a token authentication, the <API name>_token variable is created.
These variables are prefixed with the name of the imported API. They are meant to help you avoid modify the requests in case of a server change. The value of each of these variables can be modified in the Variables editor as described in Variables
Note: When importing again the same API, the variables previously created are overridden by the variables created by the new import.