Media requests
Recording
NeoLoad can record media content requests to provide simulation-specific statistics. The statistics help assess the media content display quality.
NeoLoad supports media requests issued through the HTTP and RTMP communication protocols.
HTTP protocol
In NeoLoad, a media request on the HTTP protocol is identified by the file extension or the response Content-Type. The parameters are defined in the Project Preferences panel under the Modules Manager category. For more information, see Media Streaming
To record an HTTP media request, follow these steps:
-
Start a new record.
-
Run the scenario you want to simulate subsequently.
-
Terminate the record with the post-recording wizard.
RTMP protocol
In NeoLoad, a media request on the RTMP protocol is identified when the Flash client issues the play command. The command initiates the transfer of video/audio data by the server.
To record an RTMP media request, follow these steps:
-
Start a new record after activating the RTMP protocol.
-
Run the scenario you want to simulate subsequently.
-
Terminate the record with the post-recording wizard.
Post-recording wizard
To generate statistics about the media playback, the average downstream rate of the media must be defined in NeoLoad. NeoLoad can figure out the average rate of some codecs: MPEG-4, FLV, F4V, AVI, MP3, and IceCast.
When the average downstream rate cannot be processed in NeoLoad, it is necessary to specify it for each media request. The post-recording wizard lists all the media actions which have been recorded and whose downstream rate is unavailable.
Note: To prevent NeoLoad from simulating the media playback and to make it download the file only, the Download option in the Simulation column must be selected.
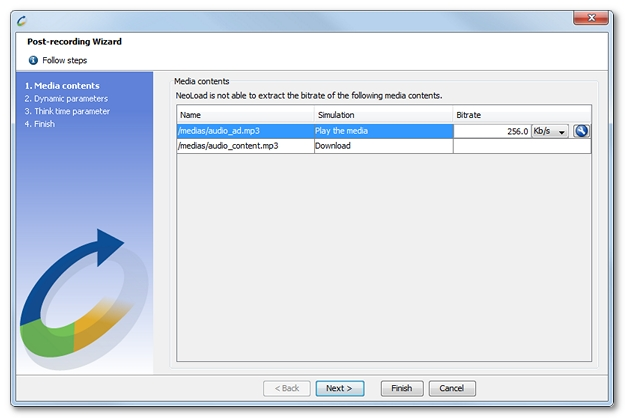
A click on the icon Compute the average bitrate makes it possible to measure the average downstream rate. The media length in seconds and the overall size of the file must be specified.
makes it possible to measure the average downstream rate. The media length in seconds and the overall size of the file must be specified.
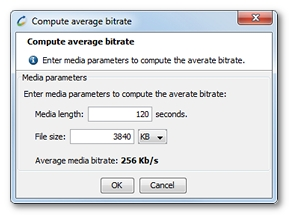
Clicking OK displays the average downstream rate determined by NeoLoad.
To measure the average downstream rate of a media, follow these steps:
-
Select the action in the list.
-
Edit the value of the Downstream column.
-
When necessary, click Compute the average bitrate
 to use the Compute average bitrate wizard.
to use the Compute average bitrate wizard.
Configure a media request
For any media request type (HTTP or RTMP), NeoLoad can be configured to process the request specifically.
The media request must be selected in the User Paths tree.
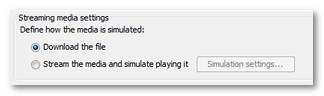
The Streaming media settings group box makes it possible to:
-
download the file like a regular resource, or
-
simulate the media playback.
Media file download
A media request can be defined to download the file when the Download the file option is selected in the Streaming media settings group box. The playback statistics are then unavailable. NeoLoad process the request like a regular one.
To configure a media request to download, follow these steps:
-
Develop the User Path tree and select a media request.
-
In Streaming media settings, select Download the file.
Media file playback
A media request can defined to simulate the media playback when the Stream the media and simulate playing it option is selected in the Streaming media settings group box. A click on the Simulation settings button displays the dialog to specify the request simulation parameters.
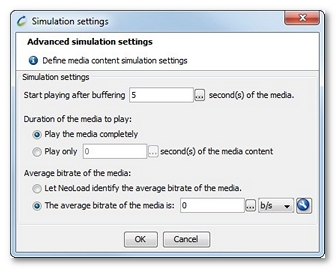
The Start playing after buffering field helps define the time spent to fill in the buffer when starting the video. The value can be a number of seconds or a variable defined with a click on the selection button.
In the Duration of the media to play group box, the time spent on simulating the media content can be defined:
-
The Play the media completely option means that the whole media is played in the load test scenario.
-
The Play only X seconds of the media content option is useful to play only an extract of the media. The value can be a number of seconds or a variable defined with a click on the selection button.
In the Average bitrate of the media group box, the stream quality of the media can be defined for the replay:
When the Let NeoLoad identify the average bitrate of the media option is selected, the average downstream rate of the media is defined by NeoLoad. NeoLoad can figure out the average rate of some codecs: MPEG-4, FLV, F4V, AVI, MP3, and IceCast.
When the average downstream rate cannot be processed in NeoLoad, it is necessary to specify it. The value for The average bitrate of the media option can be set in b/s, Kb/s, Mb/s, or Gb/s :
-
directly in the field,
-
with a variable that can be defined with a click on the selection button, or
-
with the Compute average bitrate wizard accessible with the wrench-like button. With the media length and the overall size of the file, the wizard automatically defines the bitrate. For more information, see Post-recording wizard
A click on the OK button closes the Simulation settings box. NeoLoad then downloads the file and reads it with the average downstream rate specified. Similarly to a use playing the media in a browser, NeoLoad reproduces the playback, but without displaying it.
To configure a media request to play, follow these steps:
-
Develop the User Path tree and select a media request.
-
In Streaming media settings, select Stream the media and simulate playing it.
-
Click Simulation Settings.
-
In the Simulation settings box:
-
In Start playing after bufferring, define the time in seconds to fill in the buffer.
-
In Duration of the media to play:
-
Select Play the media completely, or
-
Select and define the value for Play only X seconds of the media content to replay only an extract of the media.
-
-
In Average bitrate of the media:
-
Select Let NeoLoad identify the average bitrate of the media, or
-
Select and define the value for The average bitrate of the media to specify the simulated media stream flow for the replay.
-
-
-
Click OK.