Frameworks
In NeoLoad, dynamic parameters refer to parameters that are dynamically generated by the server and used in several requests within a scenario. This type of parameter may be used for example to manage user sessions or preserve the browsing status at any given time. These parameters, that are calculated by the server, can be inserted into a hidden field of a form, or into a URL parameter, without any input from the user.
During a load test on an application, NeoLoad simulates the traffic of hundreds of users and each of these users must be able to use the value of the parameter generated by the server as opposed to the value of the parameter recorded during the scenario creation. Normally, to manage these dynamic parameters, you need to extract the value generated by the server using a variable extractor, and re-inject it into the subsequent requests in place of the recorded value. This is not a problem when dealing with a single, isolated dynamic parameter, but it can become tedious when the dynamic parameter occurs in many requests (numerous replacements in the request definitions), or when its value changes regularly (numerous variable extractors need to be created). For more information, see Variable extractors
To make handling these parameters easier, NeoLoad includes two processes that make configuring the application dynamic parameters easier:
-
Framework dynamic parameter handling, based on predefined rules,
-
generic dynamic parameter handling, based on detection and automatic configuration.
Handle framework dynamic parameters
Within an application-specific development framework, the dynamic parameters generated by the server are often the same and are used in numerous requests. To avoid having to define variable extractors for a large number of requests, NeoLoad can search for these parameters and configure the variable extractors/replacements within the scenario.
A framework dynamic parameter allows defining rules to automate the extraction and injection of a dynamic value.
Settings
Before NeoLoad can carry out a search for framework dynamic parameters, you must define the dynamic parameters generated by the framework. You can do this through the Edit > Preferences > Frameworks menu item.
Configure dynamic parameters
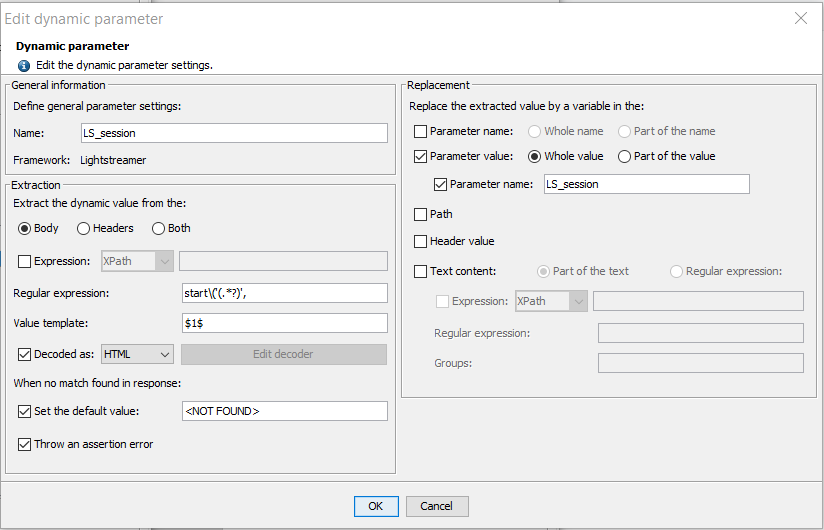
A framework dynamic parameter is made up of the following:
-
General information:
-
Name: Parameter name. This is for information purposes and must be unique.
-
Framework: Name of the framework with which the parameter is associated.
-
-
Extraction: Defines how the dynamic value is extracted from the server response.
-
Body, Headers or Both: Selects from which part of the response the parameter dynamic value is extracted.
-
Expression (optional):
-
The XPath expression option allows restricting the content extraction to one subsection within the response. XPath can only be used for HTML or XML (HTML, XML, SOAP, GWT, AMF, RTMP, Oracle Forms, Java Serialization and Siebel) -type responses.
-
The JSONPath expression option allows restricting the content extraction to one subsection within the response. JSONPath can only be used for JSON responses only (responses containing "json" in Content-Type headers).
-
-
Regular expression: Where the response contains text that corresponds to the regular expression definition, that text is extracted. The regular expression is applied to the response header or body or to the result of the XPath expression where specified.
-
Value template: The template used to assemble the value. This is an arbitrary string with specific elements that refer to the groups within the regular expression (a group is a dynamic part of the regular expression contained within parentheses): $0$ refers to the entire text matching the expression, $1$ refers to group n°1, $2$ refers to group n°2, and so on.
-
Decoded as (HTML, URL or Custom): When this option is checked, a decoder will be set on the variable extractor placed on the response. You can choose between HTML, URL and Custom decoding.
-
Edit decoder: When you have selected Value is decoded as "Custom", click this button to provide the decoding logic in JavaScript that you want to be used to decode the extracted value.
-
Set the default value: Set a default value for the variable when the definition is not matched in the server response.
-
Throw an assertion error: Treat as an assertion failure when the definition is not matched in the server response, thus causing the request to be error-flagged in the test results.
-
-
Replacement: Specifies where and how the dynamic value is injected into the request sent to the server.
-
Parameter name: Check the box if the parameter name is dynamic and contains all or part of the extracted dynamic value.
-
Parameter value: Check the box if the parameter value is dynamic and contains all or part of the extracted dynamic value. Where the parameter name is specified, only the parameters with that name are examined and, if necessary, modified.
-
Path: Use this option if the path contains the dynamic value.
-
Header value: Use this option when the values of the headers contains the dynamic value.
-
Text content: Use this option if the request text content contains all or part of the dynamic value.
-
Part of the text: All occurrences of the dynamic value are replaced in the text request.
-
Regular expression: Only replace the values that match the specified regular expression.
XPath expression (optional): The XPath expression is used to restrict the replacement to a subsection of the request. The XPath expression can only be used for HTML or XML -type requests (HTML, XML, SOAP, GWT, AMF, RTMP, Oracle Forms, Java Serialization and Siebel).
Regular expression: The expression corresponding to the string that contains or equals the extracted dynamic value.
Groups: The groups in the regular expression applied to the text content that equal the extracted dynamic value, separated by commas.
-
-
Dynamic parameter configuration example
The dynamic parameter is called id and you can assume the dynamic value extracted is 12345. The text request will be <p>The dynamic value is 12345, and not 12345.</p>.
The regular expression used for replacement will be (The dynamic value is) (\d+), (and not) (\d+).
If Groups equals 2, 4, then the request will be changed to <p>The dynamic value is ${id}, and not ${id}.</p>.
If Groups equals 2, then the request will be changed to <p>The dynamic value is ${id}, and not 12345.</p>.
Advanced usage
When certain versions of GWT are used, it can be useful to generate multiple dynamic parameters.
In this advanced usage of dynamic parameters, dollar signs are used to perform the following steps:
-
The Regular expression specified in the Extraction section is run.
-
Replacements are done in the Regular expression field of the Replacement section using dollar signs.
-
Replacements are done in the Name field using dollar signs.
-
The dynamic parameter search is done as usual.
To generate multiple dynamic parameters, follow these steps:
-
Add an extra group using parentheses in the Regular expression field of the Extraction section.
-
Use dollar signs in the Regular expression field of the Replacement section to retrieve the values of the extra group added in the Regular expression field of the Extraction section.
-
Specify a name for the parameter using dollar signs in the Name field.
-
Click OK.
Configure messages mapping
WebSocket messages mapping is configured with regular or XPath expressions. An identifier is extracted from the request and the response regular or XPath expressions to map the request and the response. Regular or XPath expressions can be specified on each framework.
Note: A framework can define only one way to extract the mapping ID from the requests, and one way to extract the mapping ID from the response, so the XPath or regular expression has to be generic enough to handle all requests and all responses.
During post-recording, NeoLoad can automatically search for WebSocket messages mapping in the recorded User Path, and pre-configure it. If the request identifier matches the response identifier, then the couple WebSocket request/response is merged into a single asynchronous action, like a plain HTTP request action.
If several requests mapping IDs match several responses mapping IDs, then the first response is linked to the first request (first-in first-out). For example, if NeoLoad detects sequentially request1, request2, response1, response2 as asynchronous calls with the same mapping ID, then request1/response1 are coupled, and request2/response2 are coupled. This will create two WebSocket asynchronous actions.
To access the Edit Messages mapping screen, in the Frameworks settings section, select a Framework, enable the WebSocket checkbox and click on the wrench-like button.
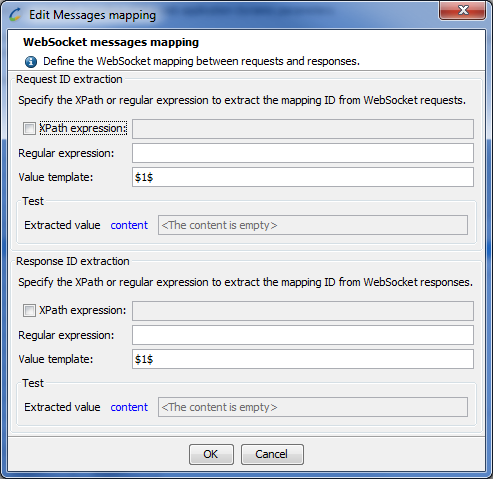
-
Request ID extraction: Defines how the mapping ID is extracted from the request.
-
XPath expression (optional): The XPath expression option allows restricting the content extraction to one subsection within the request. XPath can only be used for HTML or XML (HTML, XML, SOAP, GWT, AMF, RTMP, Oracle Forms, Java Serialization and Siebel) -type request.
-
Regular expression: Where the request contains text that corresponds to the regular expression definition, that text is extracted. The regular expression is applied to the request or to a subpart of the request extracted by the XPath expression where specified.
-
Value template: The template used to assemble the value. This is an arbitrary string with specific elements that refer to the groups within the regular expression (a group is a dynamic part of the regular expression contained within parentheses): $0$ refers to the entire text matching the expression, $1$ refers to group n°1, $2$ refers to group n°2, and so on.
-
-
Response ID extraction: Defines how the mapping ID is extracted from the response.
-
XPath expression (optional): The XPath expression option allows restricting the content extraction to one subsection within the response. XPath can only be used for HTML or XML (HTML, XML, SOAP, GWT, AMF, RTMP, Oracle Forms, Java Serialization and Siebel) -type responses.
-
Regular expression: Where the response contains text that corresponds to the regular expression definition, that text is extracted. The regular expression is applied to the response or to a subpart of the response extracted by the XPath expression where specified.
-
Value template: The template used to assemble the value. This is an arbitrary string with specific elements that refer to the groups within the regular expression (a group is a dynamic part of the regular expression contained within parentheses): $0$ refers to the entire text matching the expression, $1$ refers to group n°1, $2$ refers to group n°2, and so on.
-
Manage frameworks
Framework dynamic parameters are organized by frameworks. A framework is a set of dynamic parameters that are specific to a web application or family of web applications (for example, .NET).
Certain predefined frameworks also contain rules for handling Push-type requests. When a framework is selected in the interface, NeoLoad displays the support of the different Push technologies, polling or streaming. These handling rules are neither visible nor editable. For more information, see Push frameworks.
To add a framework, follow these steps:
-
Click on the + button to the right of the Framework table.
-
Enter the Framework name in the Framework field.
-
Click OK.
Note: A framework name is unique.
To edit a framework name, follow these steps:
-
In the Framework table, double-click on the framework name to be edited.
-
Edit the framework name using the keyboard.
-
Hit ENTER to confirm the change.
Note: Push frameworks cannot be renamed.
To delete a framework, follow these steps:
-
Select the framework in the Framework table.
-
Click on the - button to the right of the Framework table.
Note: Deleting a framework also deletes all its associated dynamic parameters.
Manage frameworks dynamic parameters
You can add, edit and delete framework dynamic parameters, just as regular frameworks, using the procedures described hereinafter.
The simplest way to define a framework dynamic parameter is to set a variable extractor on one of the requests whose server response contains the dynamic parameter and then convert the extractor into a framework dynamic parameter:
To create a framework dynamic parameter using a variable extractor, follow these steps:
-
In the User Path, select the request whose response contains the dynamic parameter.
-
Click on the Advanced button.
-
Select the Variable extractors tab.
-
Click on the + button to add a variable extractor.
-
Define a variable extractor to enable the dynamic value extraction (give the variable the name of the dynamic parameter). For more information, see Create a variable extractor
-
Select the extractor in the list of variable extractors.
-
Click on the Add to framework parameters button.
-
Enter the parameter name and the framework name (you may use an existing framework or enter the name of a new framework), then click Next.
-
Configure the replacement settings for the dynamic parameter, then click Next.
-
Launch a dynamic parameter search for NeoLoad to set the remaining extractors required and to replace the parameter value with the extracted value
This extractor is now added to the list of framework parameters. When future dynamic parameter searches are carried out (after the next recording for example), NeoLoad will be able to configure the extractors automatically and replace the static value in the requests with the extracted variable.
Using a variable extractor to add a dynamic parameter provides an easy way to configure the regular expression and the template to apply to find the parameter.
To create a framework parameter from the Preferences, follow these steps:
-
Go to the Frameworks section in the Global Preferences.
-
Select the framework in which you want to create the parameter.
-
Click on the + button to the right of the framework parameters table.
-
Enter the required information, and click OK.
To edit a framework parameter from the , follow these steps:
Go to the Frameworks section in the Global Preferences.
Select the framework containing the parameter.
Select the framework parameter to be edited.
Click on the framework parameter editing button.
When you have finished editing the parameter, click OK to confirm.
Import/Export
The Export button can be used to export the required parameters to the selected directory with an XML file for each framework.
The Import button can be used to import a previously-exported XML file or to import the parameters created in a previous version and available in the Controller_user.properties file in the user directory.