Data model
Each request from a client to the server must contain all the necessary information to allow the server to understand the query.
The Controller receives Entry objects defined by a Status and associated to a Session containing Context information. The data model can be defined as following:
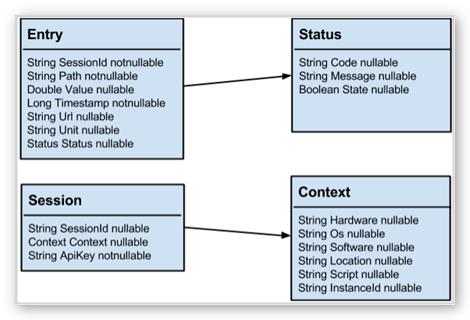
The following examples illustrate a typical request and response for creating session and entries:
Request:
POST http://localhost:7400/DataExchange/v1/Service.svc/Session HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
Host: localhost:7400
Content-Length: 186
{
"d": {
"Context": {
"Hardware": "iphone",
"Os": "myOs",
"Software": "mySoftware",
"Location": "myLocation",
"Script": "myScript",
"InstanceId": "1"
}
}
}Response:
HTTP/1.1 201 Created
Content-Type: application/atom+xml;charset=utf-8;type=entry
DataServiceVersion: 2.0
Date: Fri, 10 Oct 2014 14:38:31 GMT
Location: http://localhost:7400/DataExchange/v1/Service.svc/Session('')
Content-Length: 450
{
"d":{
"__metadata":{
"id":"http://localhost:7400/DataExchange/v1/Service.svc/Session('')",
"uri":"http://localhost:7400/DataExchange/v1/Service.svc/Session('')",
"type":"com.neotys.rest.dataexchange.model.Session"
},
"SessionId":"a2f30f8e-943a-4957-98f6-6c406bc1b4c0",
"Context":{
"__metadata":{
"type":"com.neotys.rest.dataexchange.model.Context"
},
"Hardware":"iphone",
"Os":"myOs",
"Software":"mySoftware",
"Location":"myLocation",
"Script":"myScript",
"InstanceId":"1"
},
"ApiKey":""
}
}The "SessionId" is provided in the server response. It has to be extracted to be used in further Entry creation.
Note: If an identification is required on the Controller side, the -APIKey parameter must be included in the command. For more information about the identification, see REST APIs.
Request:
POST http://localhost:7400/DataExchange/v1/Service.svc/Session HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
Host: localhost:7400
Content-Length: 206
{
"d": {
"Context": {
"Hardware": "myHardware",
"Os": "myOs",
"Software": "mySoftware",
"Location": "myLocation",
"Script": "myScript",
"InstanceId": "1"
},
"ApiKey": "myApiKey"
}
}Response:
HTTP/1.1 201 Created
Content-Type: application/atom+xml;charset=utf-8;type=entry
DataServiceVersion: 2.0
Date: Fri, 10 Oct 2014 14:40:48 GMT
Location: http://localhost:7400/DataExchange/v1/Service.svc/Session('myApiKey')
Content-Length: 474
Server: Jetty(9.1.2.v20140210)
{
"d":{
"__metadata":{
"id":"http://localhost:7400/DataExchange/v1/Service.svc/Session('myApiKey')",
"uri":"http://localhost:7400/DataExchange/v1/Service.svc/Session('myApiKey')",
"type":"com.neotys.rest.dataexchange.model.Session"
},
"SessionId":"a2f30f8e-943a-4957-98f6-6c406bc1b4c0",
"Context":{
"__metadata":{
"type":"com.neotys.rest.dataexchange.model.Context"
},
"Hardware":"iphone",
"Os":"myOs",
"Software":"mySoftware",
"Location":"myLocation",
"Script":"myScript",
"InstanceId":"1"
},
"ApiKey":"myApiKey"
}
}The "SessionId" is provided in the server response. It has to be extracted to be used in further Entry creation.
Request:
POST http://localhost:7400/DataExchange/v1/Service.svc/Entry HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
Host: localhost:7400
Content-Length: 286
{
"d": {
"SessionId": "a2f30f8e-943a-4957-98f6-6c406bc1b4c0",
"Path": "metric|node1",
"Value": "70.0",
"Timestamp": "1412953615000",
"Url": "url1",
"Unit": "unit1",
"Status": {
"Code": "code1",
"Message": "message1",
"State": "FAIL"
}
}
}Response:
HTTP/1.1 201 Created
Content-Type: application/atom+xml;charset=utf-8;type=entry
DataServiceVersion: 2.0
Date: Fri, 10 Oct 2014 14:40:49 GMT
Location: http://localhost:7400/DataExchange/v1/Service.svc/Entry('ca5788a8-437c-47e1-ba5c-2bd5ee30b247')
Content-Length: 529
Server: Jetty(9.1.2.v20140210)
{
"d":{
"__metadata":{
"id":"http://localhost:7400/DataExchange/v1/Service.svc/Entry('a2f30f8e-943a-4957-98f6-6c406bc1b4c0')",
"uri":"http://localhost:7400/DataExchange/v1/Service.svc/Entry('a2f30f8e-943a-4957-98f6-6c406bc1b4c0')",
"type":"com.neotys.rest.dataexchange.model.Entry"
},
"SessionId":"a2f30f8e-943a-4957-98f6-6c406bc1b4c0",
"Path":"metric|node1",
"Value":"70.0",
"Timestamp":"1412953615000",
"Url":"url1",
"Unit":"unit1",
"Status":{
"__metadata":{
"type":"com.neotys.rest.dataexchange.model.Status"
},
"Code":"code1",
"Message":"message1",
"State":"FAIL"
}
}
}Request:
POST http://localhost:7400/DataExchange/v1/Service.svc/Entries HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
Host: localhost:7400
Content-Length: 589
{
"d": {
"results": [
{
"SessionId": "a2f30f8e-943a-4957-98f6-6c406bc1b4c0",
"Path": "metric|node1",
"Value": "70.0",
"Timestamp": "1412953616000",
"Url": "url1",
"Unit": "unit1",
"Status": {
"Code": "code1",
"Message": "message1",
"State": "FAIL"
}
},
{
"SessionId": "a2f30f8e-943a-4957-98f6-6c406bc1b4c0",
"Path": "metric|node2",
"Value": "70.0",
"Timestamp": "1412953616000",
"Url": "url1",
"Unit": "unit1",
"Status": {
"Code": "code1",
"Message": "message1",
"State": "FAIL"
}
}
]
}
}Response:
HTTP/1.1 201 Created
Content-Type: application/atom+xml;charset=utf-8;type=entry
DataServiceVersion: 2.0
Date: Fri, 10 Oct 2014 14:52:00 GMT
Content-Length: 1075
Server: Jetty(9.1.2.v20140210)
{
"d":{
"results":[
{
"__metadata":{
"id":"http://localhost:7400/DataExchange/v1/Service.svc/Entries('a2f30f8e-943a-4957-98f6-6c406bc1b4c0')",
"uri":"http://localhost:7400/DataExchange/v1/Service.svc/Entries('a2f30f8e-943a-4957-98f6-6c406bc1b4c0')",
"type":"com.neotys.rest.dataexchange.model.Entry"
},
"SessionId":"a2f30f8e-943a-4957-98f6-6c406bc1b4c0",
"Path":"metric|node1",
"Value":"70.0",
"Timestamp":"1412953616000",
"Url":"url1",
"Unit":"unit1",
"Status":{
"__metadata":{
"type":"com.neotys.rest.dataexchange.model.Status"
},
"Code":"code1",
"Message":"message1",
"State":"FAIL"
}
},
{
"__metadata":{
"id":"http://localhost:7400/DataExchange/v1/Service.svc/Entries('a2f30f8e-943a-4957-98f6-6c406bc1b4c0')",
"uri":"http://localhost:7400/DataExchange/v1/Service.svc/Entries('a2f30f8e-943a-4957-98f6-6c406bc1b4c0')",
"type":"com.neotys.rest.dataexchange.model.Entry"
},
"SessionId":"a2f30f8e-943a-4957-98f6-6c406bc1b4c0",
"Path":"metric|node2",
"Value":"70.0",
"Timestamp":"1412953616000",
"Url":"url1",
"Unit":"unit1",
"Status":{
"__metadata":{
"type":"com.neotys.rest.dataexchange.model.Status"
},
"Code":"code1",
"Message":"message1",
"State":"FAIL"
}
}
]
}
}Fields details
No maximum length is enforced on any string.
Note about time synchronization that to make sure the entries sent to the Controller have the appropriate timestamps, the clocks of the NeoLoad Controller, EuE platform, and all devices used must be synchronized.
Note: If a user sends an entry containing a path with a forbidden characters, then the characters will be escaped on the server side (which consists in replacing any forbidden characters with '_') and no warning message will be logged. Forbidden characters are: '£', '?', '$', '\"', '[', ']', '<', '>', '|', '*', '¤', '?', '§', ‘'µ', '#', '`', '@', '^', '²', '°', '¨'
Session
-
SessionId is a unique identification string send by the server in the response.
-
ApiKey is a string defined by the user.
-
Context: Contains the Context class objects.
Context
-
Hardware (optional): Hardware details (iPhone, Windows Phone, etc.)
-
Os (optional): OS details (iOS 7.0, Android 4.2, etc.)
-
Software (optional): Software details.
-
Location (optional): Location information.
-
Script (optional): Script information.
-
InstanceId (optional) identifies the instance.
Entry
-
SessionId is a unique identification string send by the server in the session creation response.
-
Value: Entry value.
-
Url: Uniform Resource Identifier.
-
Timestamp is an absolute time used to synchronize the entry with NeoLoad data.
-
Path is a string representing the list of nodes that contains the statistics.
-
State (optional) is an enumeration with only 2 values: PASS / FAIL.