Variable extractors
A variable extractor extracts a string from the server response to the request and assigns the string to a variable. The variable extractor features two operating modes:
Simple mode: The user defines the string to be extracted.
Advanced mode: The user can define more complex extractions using regular expressions.
The Definition group box (simple mode) allows defining the extractor.
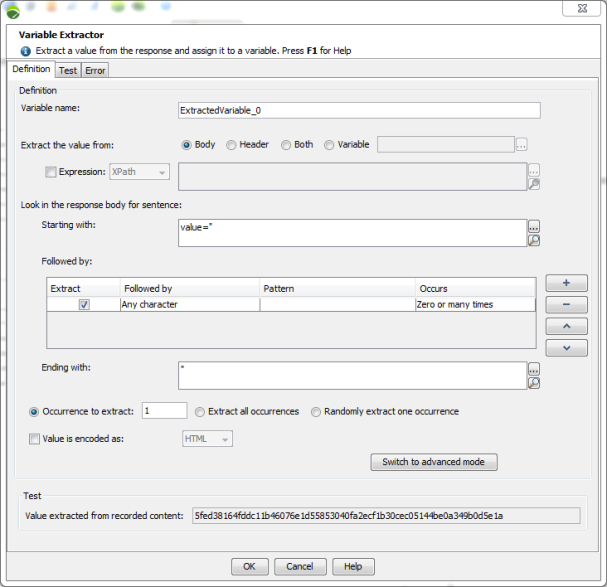
Variable name: The name of the variable automatically created to contain the value extracted. You need to use the expression ${VariableName}, which NeoLoad will replace with the value during the test.
Extract the value from: Extracts the value from either the body, the headers or both of the server response or the content of a NeoLoad variable. Extracting a variable from the content of another variable allows extracting a content in several steps. First extracts a part of the response based on a regular expression, then uses another regular expression to extract a part of that.
Expression: Ticking the check box allows selecting a node in the XML or JSON format response. The list box allows you to select the appropriate format. However, NeoLoad automatically detects the format and selects it accordingly.
Note: The extractors are ordered and executed in the order they are defined. You can re-order the extractors using the arrow buttons.
Note: Extraction using an XPath expression is only available for HTML and XML responses, as well as for SOAP, GWT, Adobe Flex/AMF, Oracle Forms, Java Serialization, RTMP, Siebel and Silverlight responses. For more information, see Extract variables in an XML response.
Note: Extraction using a JSONPath expression is only available for JSON responses. JSON responses contain "json" in Content-Type headers. For more information, see Extract variables in a JSON response.
Starting with: The phrase in the server response appearing immediately before the value to be extracted.
Followed by: The definition of the string main body. The extracted string is the concatenation of all the parts selected for extraction.
Ending with: The phrase in the server response appearing immediately after the value to be extracted.
Occurrence to extract: If the definition is matched more than once, select the occurrence to be used. The default value is "1" (use the first occurrence) but you can choose to use a random occurrence or all occurrences (useful with loops).
If you choose to process all the matched occurrences, the following variables are automatically created:
<VariableName>_matchNr- the number of occurrences found; can be 0.<VariableName>_n, where n = 1,2,3 and so on. - the strings as generated by the value template.<VariableName>_n_gm, where m=1,2 - the groups matching.<VariableName>- always attached to the default value.<VariableName>_rand, random string from generated strings.<VariableName>randgm, where m=0,1,2 - the groups matching rand.<VariableName>_json, the string value of the JSON array, containing all the extracted occurrences.
Value is encoded as: When this option is checked, a decoder is applied on the value before it is placed in the variable. You can choose between HTML, URL and Custom decoding.
Example with HTML: With the string start&end extracted from the server response, the value in the NeoLoad variable will be start&end if the option is checked, and start&end if the option is not checked.
Edit decoder: When you have selected Value is encoded as "Custom", click this button to provide the decoding logic in JavaScript that you want to be used to decode the extracted value.
In the Test zone, the Value extracted from recorded content field displays the result of the current extractor applied to the recorded content. If not defined, it can be modified manually in the Recorded response tab of Advanced parameters or through the Update recorded content.
Note: When switching to advanced mode, the definition is automatically converted from simple to advanced.
The Definition group box (advanced mode) allows performing the extraction on the server response using a regular expression.
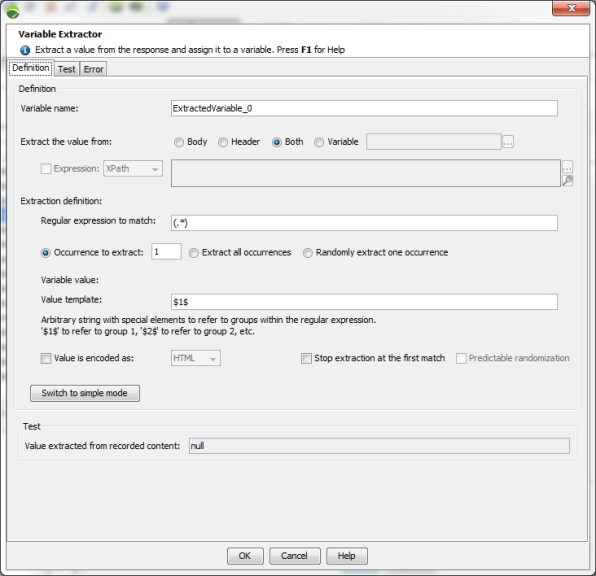
Variable name: The name of the variable automatically created to contain the value extracted.
Extract the value from: Extracts the value from either the body of the server response, XML nodes NeoLoad using XPath expression, the headers of the server response or both, or the content of a NeoLoad variable . Extracting a variable from the content of another variable, allows extracting a content in several steps. First extract a part of the response based on a regular expression, then use another regular expression to extract a part of it.
Expression: Ticking the check box allows selecting a node in the XML or JSON format response. The list box allows you to select the appropriate format. However, NeoLoad automatically detects the format and selects it accordingly.
Note: The extractors are ordered and executed in the order they are defined. You can re-order the extractors using the arrow buttons.
Note: Extraction using an XPath expression is only available for HTML and XML responses, as well as for SOAP, GWT, Adobe Flex/AMF, Oracle Forms, Java Serialization, RTMP, Siebel and Silverlight responses. For more information, see Extract variables in an XML response.
Note: Extraction using a JSONPath expression is only available for JSON responses. JSON responses contain "json" in Content-Type headers. For more information, see Extract variables in a JSON response.
Regular expression to match: The regular expression used to extract the value. Within the expression, the parts to be extracted must be enclosed in brackets (valid: value="(.+?)", invalid: value=".+?"). For more information, see Regular expressions.
Occurrence to extract in the page: If the definition is matched more than once, select the occurrence to be used. The default value is "1" (use the first occurrence) but you can choose to use a random occurrence or all occurrences (useful with loops).
If you choose to process all the matched occurrences, the following variables are automatically created:
<VariableName>_matchNr- the number of occurrences found; can be 0.<VariableName>_n, where n = 1,2,3 and so on. - the strings as generated by the value template.<VariableName>_n_gm, where m=1,2 - the groups matching.<VariableName>- always attached to the default value.<VariableName>_rand, random string from generated strings.<VariableName>randgm, where m=0,1,2- the groups matching rand.<VariableName>_json, the string value of the JSON array, containing all the extracted occurrences.
Value template: The template used to construct the value. This is an arbitrary string containing special elements that refer to groups within the regular expression (a group is a dynamic portion of the regular expression set within brackets): $0$ refers to the entire text matching the expression, $1$ refers to group 1, $2$ refers to group 2, and so on. Using an illegal group will cause the extraction to fail and the value <NL-Illegal-groupIndex> will be set in the variable during the test. This typically arises when no brackets are specified in the regular expression to be matched.
Value is encoded as: When this option is checked, a decoder is applied on the value before it is placed in the variable. You can choose between HTML, URL and Custom decoding.
Example with HTML: With the string start&end extracted from the server response, the value in the NeoLoad variable will be start&end if the option is checked, and start&end if the option is not checked.
Edit decoder: When you have selected Value is encoded as "Custom", click this button to provide the decoding logic in JavaScript that you want to be used to decode the extracted value.
Note: When switching to simple mode, the last simple definition is used, since advanced-simple conversion is impossible.
Stop extraction at the first match: This option allows considering the first value extracted for a looping request. When this option is selected, the variable extractor is stopped as soon as an extraction is done. The behavior is local to every Virtual User.
Predictable randomization. When this option is selected, randomly generated values have comparable values for two identical tests. Randomization returns the same values set per Virtual User.
In the Test zone, the Value extracted from recorded content field displays the result of the current extractor applied to the recorded content. If not defined, it can be modified manually in the Recorded response tab of Advanced parameters or through the Update recorded content.
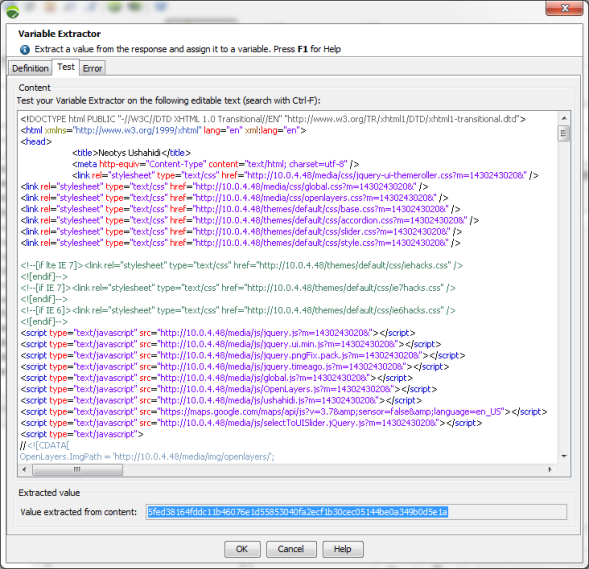
Test Variable Extractor
The Test tab of the Variable Extractor dialog box allows testing the Variable Extractor. Enter the text corresponding to the server response in the text box and check the behavior from the Value extracted from content field. Note that the modified text is lost when closing the dialog.
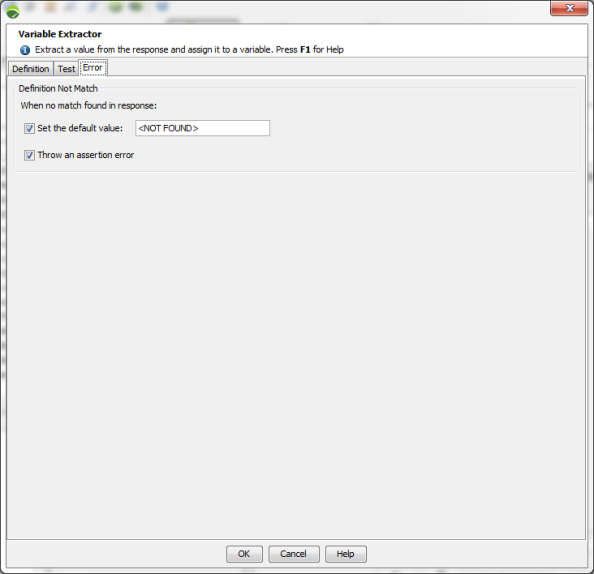
Manage errors in server response
The Error tab in the Variable Extractor dialog box allows specifying the action to perform if the definition is not matched in the server response. Two choices are available:
Set a default value for the variable.
Treat as an assertion failure, thus causing the request to be error-flagged in the test results
Edit an HTTP Request response for easier handling of Variable Extractor
Editing an HTTP Request response may be useful to use more easily the Variable Extractor.
The response of an HTTP request can be edited in three different ways:
By editing the recorded response content of the request as described in Advanced parameters and the Recorded response tab section.
By updating the recorded content of your User Path as described in Update recorded content.
By providing a response content when manually creating an HTTP request as described in Create an HTTP request.
Example of a variable extractor
Given the following content Your order number Mr Smith is:12345 and that the string to be extracted is 12345 to be used in a subsequent request.
The Variable Extractor is defined with:
Variable name: "MyVariable"
Extract from: "Message body"
Regular expression to be matched: "Your order number(.+)? is:([0-9]+);"
Value template: "$2$" as it is the order number that must be extracted and not the name of the person.
Occurrence within the page: "1"
Use $1$ to obtain the name. ($0$ would return the complete matched text: "Your order number Mr Smith is:12345;")
Default value: "-1" for example.
The Variable Extractor is defined thus:
Extract from: "Header"
Regular expression to be matched: "MyHeader: (.*)"
Occurrence within page: "1"
Value template:"$1$"
Individual group extraction
When the regular expression contains several groups, it is possible to access the value of each indidual group by appending "_gm" at the end of the variable name ("m" being the group number):
<VariableName>_gmfor single extraction variable,<VariableName>_n_gmfor multiple extraction variable.
For example, with response:
name=value1;name=value2
name=value3;name=value4and regular expression
name=(.*?);name=(.*?)For single extraction variable:
- ${<VariableName>_g0} evaluates to name=value1;name=value2
- ${<VariableName>_g1} evaluates to value1
- ${<VariableName>_g2} evaluates to value2For multiple extraction variable:
- ${<VariableName>_1_g0} evaluates to name=value1;name=value2
- ${<VariableName>_1_g1} evaluates to value1
- ${<VariableName>_1_g2} evaluates to value2
- ${<VariableName>_2_g0} evaluates to name=value3;name=value4
- ${<VariableName>_2_g1} evaluates to value3
- ${<VariableName>_2_g2} evaluates to value4Extract variables in a JSON response
The procedure for extracting variables in JSON-format response is almost identical to the standard procedure.
Variable extractors may be defined on a JSON node.
The following screenshots show the simple and advanced variable extraction modes.
In simple mode:
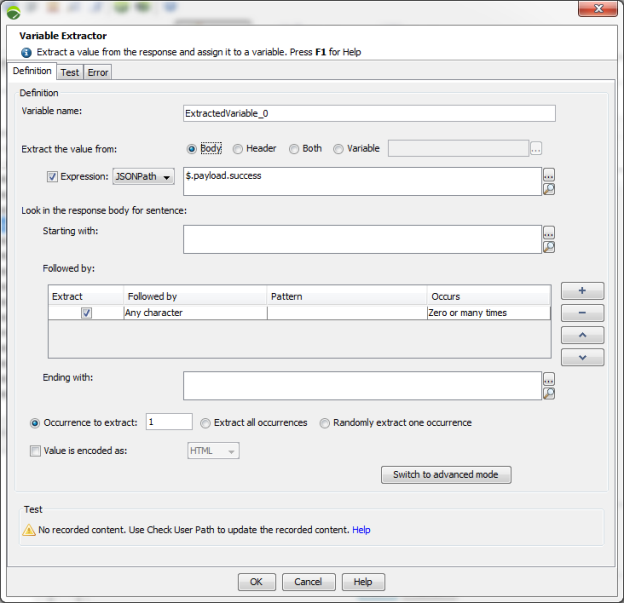
In advanced mode:
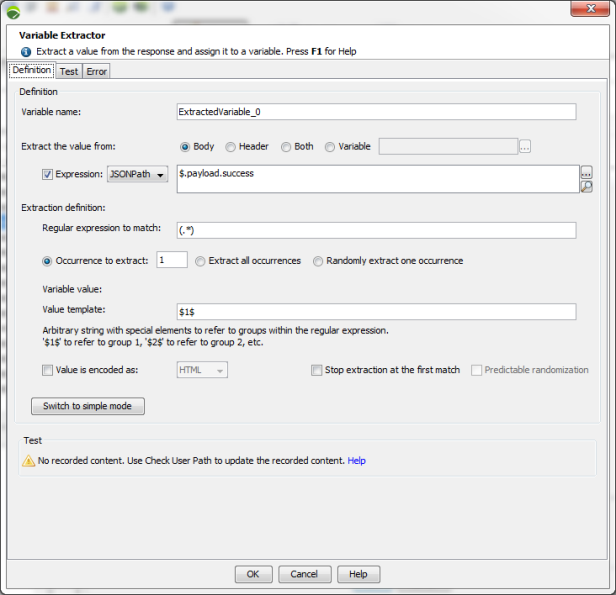
To create a variable extractor using JSONPath, follow these steps:
Create an extractor.
Tick the Expression check box.
In the list box, select JSONPath.
Click on the magnifying glass next to the text field, and select the JSON node to be extracted.
Click OK.
The JSONPath expression for the selected node appears in the text field.
Define your extractor on the JSON node text.
Note: Extracting variables on a JSON node are resource-consuming operations. Only use this type of extraction if absolutely necessary.
Extract variables in an XML response
The procedure for extracting variables in XML-format response is almost identical to the standard procedure.
Variable extractors may be defined on an XML node.
The following screenshots show the simple and advanced variable extraction modes.
In simple mode:
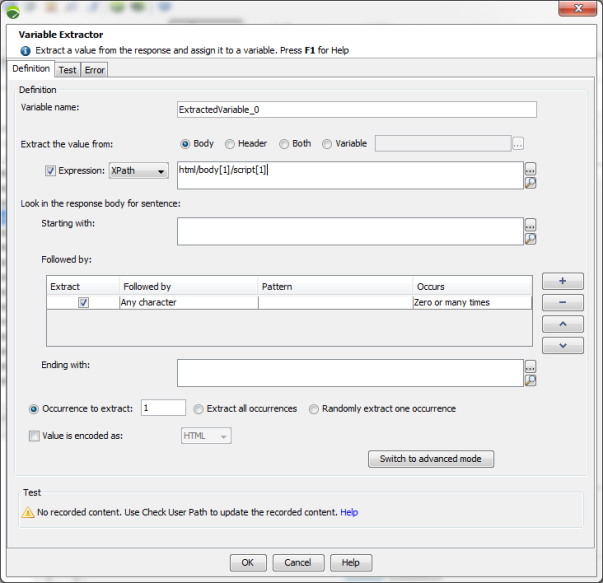
In advanced mode:
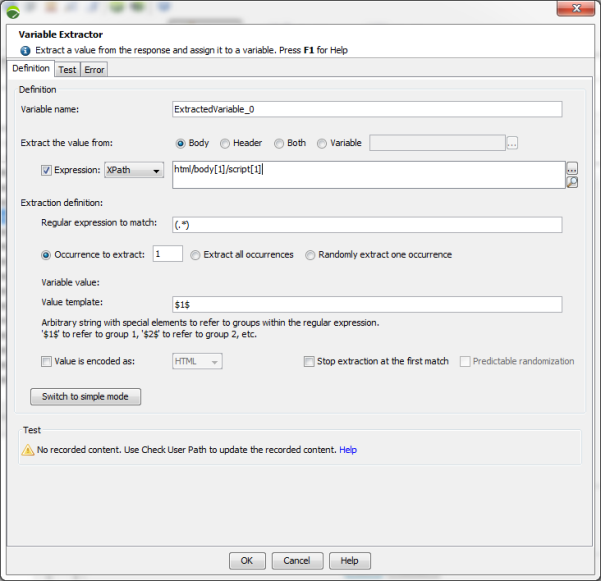
To create a variable extractor using XPath, follow these steps:
Create an extractor.
Tick the Expression check box.
In the list box, select XPath.
Click on the magnifying glass next to the text field, and select the XML node to be extracted.
Click OK.
The XPath expression for the selected node appears in the text field.
Define your extractor on the XML node text.
Note: Extracting variables on an XML node are resource-consuming operations. Only use this type of extraction if absolutely necessary.