Statistics measurement
The definitions below explain how the main statistics are measured by NeoLoad.
Count
Count statistics for pages/transactions/requests are the number of full executions. When a page/transaction/request is interrupted (because of error or end of test), then the count number is not incremented.
Request response time
NeoLoad response time is measured from the time the first byte of a request is sent, until the time the last byte of the response is received, namely including network time to send request and receive response.
It includes DNS resolution time, connection time, SSL handshake time. It does not include think time, time to create the request nor time to wait for an available socket.
When two requests are sent over the same connection, the connection establishment time is only included in the first request response time. As a result, when connection is kept alive through several requests, it is common to have a higher response time on the first request, as it includes connection initialization operated once.
By default, browser parallel connection per host is equal to 6 (can be customized), so it is common to have the 6 first request execution with higher response time.
Web page response time/duration
Web page response time is the time to execute all requests of a page, measured from the time the first byte of the first request is sent, until the time all responses are received. It includes network time to send all requests and receive all responses.
The number of connections available on the population browser settings, and the page playback settings have an impact on the way nested requests are executed, and thus on the Web page response time measured.
Number of connections
The number of simultaneous HTTP1 connections that can be opened on the remote server by one Virtual User can be configured on the population browser settings (see Browser profile). If the Virtual User needs to execute more requests than the number of available connections to a server, then the request execution is paused until a connection becomes available. In NeoLoad, each Virtual User has by default a pool of 6 connections per remote server.
Requests playback
The requests nested under a Web page can be executed either in parallel, or sequentially (see Web Pages).
-
Executing requests in parallel is conform to the HTTP standard, and this what is done by most browsers, and namely NeoLoad does it by default. When executing pages in parallel, NeoLoad will start by executing the first request (typically entry point like HTML page), wait to fully receive the response, and then execute all other requests in parallel, according to the number of connections available per server. As a result, the first resource of a Web page is always executed in single thread, before the parallel execution starts for other resources.
-
Executing requests sequentially ensures that requests be played one after the other, not more than one at a time, and according to the order specified in the Web page. If the browser is configured to have several connections to the server, there is no guarantee that the same connection will be used for all requests.
Transaction duration
Transaction duration is the time to execute all elements within the transaction. It includes response times of all nested resources (including delays and excluding think times).
Userpath duration
Userpath duration is the time to execute all elements within the userpath. It includes the duration of the Init container execution, the sum of the duration of each Actions containers execution, and the duration of the End container execution. Userpath duration includes delays time and excludes think times.
Minimum/Maximum response time measures
The minimum and maximum response time statistics are measured for each request, page and transaction, and aggregated per time interval.
Time interval
Length of time interval is defined based on the scenario duration policy. Duration policies with “no limit” or “by iteration” have a fix interval of 5 seconds. Otherwise, time duration policy depends on the duration of the scheduled test.
For tests scheduled to last:
-
less than 1 hour, time interval is 1 second
-
less than 5 hours, time interval is 5 seconds
-
less than 12 hours, time interval is 10 seconds
-
less than 24 hours, time interval is 30 seconds
-
less than 48 hours, time interval is 60 seconds
-
less than 96 hours, time interval is 120 seconds
-
more than or 96 hours, time interval is 240 seconds
The length of time interval based on the test duration is an advanced setting that can be edited in the file conf/controller.properties located in the installation directory of NeoLoad.
In section Compact:
[Compact]
0=1
60=5
300=10
720=30
1440=60
2880=120
5760=240Min/Max statistics correlation between requests, pages and transactions
There is no direct correlation between min/max statistics across requests, pages and transactions:
-
The sum of all minimum request response times of a web page is not the minimum page response time.
-
The sum of all maximum request response times of a web page is not the maximum page response time.
-
The sum of all request response times of a web page is not the page response time.
-
The sum of all minimum page response times of a transaction is not the minimum transaction response time.
-
The sum of all maximum page response times of a transaction is not the maximum transaction response time.
-
Within the same time interval, execution of a request might be the minimum of all duration, and yet the parent page is the maximum duration.
Example
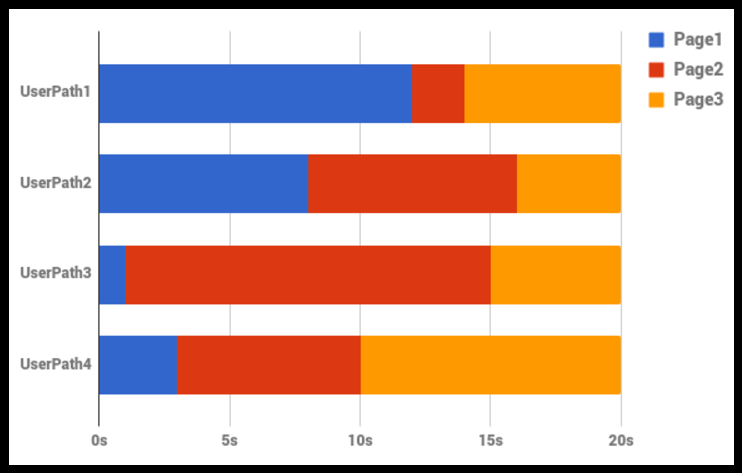
Let's consider the example below. This example represents 4 User Paths with three pages per run.
Each User Path lasts for 20 seconds. So the min and max of a full User Path equal 20 seconds. However the sum of minimum duration per page is 10 seconds and sum of maximum duration per page is 44 seconds.
Same example works with requests and pages.
TTFB duration
The “Time To First Byte” duration is the elapsed time between the time the element started and the time the first byte is received:
-
Request TTFB is the elapsed time between sending the first byte of the request and receiving the first byte of the response.
-
Page TTFB is the elapsed time between sending the first byte of the first request and receiving the first byte of the first request response.
-
Transaction TTFB is the elapsed time between the time the transaction started and the time the first byte is received. Transaction TTFB includes duration before executing the first request (delay, think times…).
-
User Path TTFB is the elapsed time between the time the Virtual User started and the time the first byte is received. User Path TTFB includes duration before executing the first request (delay, think times…).