Adobe RTMP requests
Note: This feature uses Adobe Flex libraries, which NeoLoad no longer supports due to security concerns. If you wish to continue using this feature at your own discretion, please reach out to Tricentis support for help getting it back.
RTMP is a binary client-server data transfer protocol used by certain Adobe Flash applications. The optional Adobe RTMP (Real Time Messaging Protocol) module allows load testing Adobe Flash applications programmed using the Adobe RTMP technology.
There are several versions of the RTMP binary protocol:
-
RTMP, the basic data transfer protocol that works on top of TCP/IP;
-
RTMPT, RTMP protocol encapsulated within the HTTP protocol requests/responses;
-
RTMPS, identical to RTMPT but using HTTPS.
-
RTMPE, RTMP protocol encrypted using proprietary Adobe algorithms. This protocol is not supported by NeoLoad.
Note: To be able to handle RTMP requests, you will need to purchase the optional Adobe RTMP and Adobe AMF modules. These modules are included in the demo version of NeoLoad.
Recording a RTMP application in NeoLoad is subject to certain limitations. For more information, see Limitations.
Note: To communicate with the server using RTMPT, the Flash client uses the system proxy settings, not the browser settings. With Windows, and when recording with a browser other than Internet Explorer, the Internet Explorer proxy settings must be changed for NeoLoad to be able to see the RTMPT requests.
Dependent libraries
When recording RTMP-type requests, you will need to load the Java classes for the objects exchanged. For more information, see Adobe RTMP.
Recording
The following diagram shows how the Adobe RTMP module works during recording:
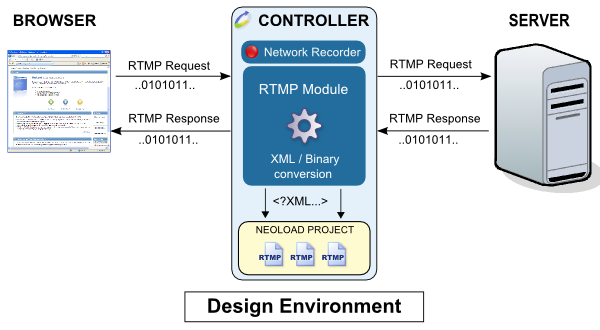
The RTMP data exchanged between the client and server is captured by NeoLoad. The Adobe RTMP module comes into play, analyzing and decoding the requests. Once translated into XML, the requests are inserted in the project.
Runtime
The following diagram shows how the Adobe RTMP module works during a test run:
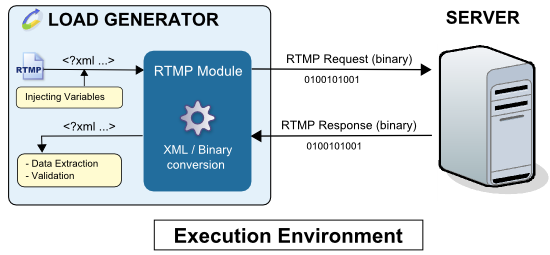
The XML request variables are evaluated and the module engine translates the XML to binary data. This data is then sent to the server. The binary response received is translated into XML and the validity checks and Variable Extractors of the played request are executed.
RTMP channel
RTMP channels are requests with special characteristics:
-
The client does not send any requests, the channel being created upon connecting to the server.
-
The server sends multiple responses through the channel.
-
It is identified by a specific icon in the User Path actions.
The way these requests behave has an impact on the User Path design:
-
The RTMP channel activity is suspended pending the next server response, that is to say it prevents the Virtual User continuing its execution thread as long as the response has not been received.
-
Each time a response is received, the variable extractors and assertions placed on the request are executed.
At the end of the recording, NeoLoad detects the presence of the RTMP channel and offers to create a new version of the User Path. This is an example of a User Path created with an RTMP channel:
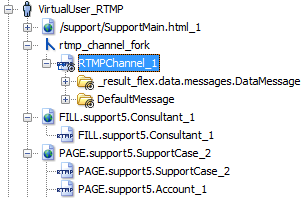
The RTMPChannel_1 logical action is used to execute the RTMP channel in a secondary execution channel in the User Path. For more information, see Fork.
NeoLoad handles Push technologies, including RTMP. For more information about the Push technologies supported by NeoLoad, Push frameworks and RTMP streaming. For more information about streaming, see Streaming requests.
Post-recording wizard
At the end of recording, the JAR declaration panel is displayed if any externalized objects have missing Java classes:
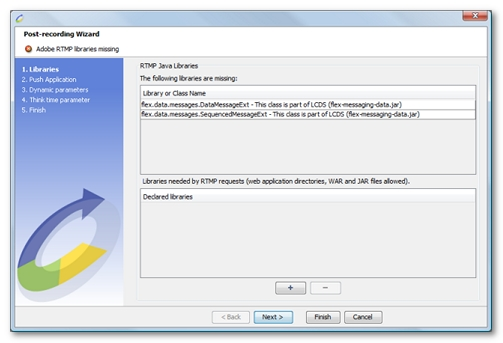
-
Externalizable objects (which extend java.io.Externalizable in Java) are objects that are responsible for saving and restoring the contents of their instances themselves.
-
All the classes for the externalizable objects sent must be loaded.
-
This panel only displays part of the missing classes; not all the missing classes can be resolved.
To declare the missing Java RTMP libraries (JAR files), follow these steps:
-
Open the file explorer by clicking the + button.
-
Select an appropriate WAR file for the application, or the directory containing the deployed web application, then click Select. NeoLoad automatically retrieves the required JAR files from the selected application. You also may select the JAR files to be loaded manually in NeoLoad. Repeat the operation as many times as is necessary.
-
A message confirms the declaration. If the operation fails, make sure that all the required Java RTMP libraries have been declared.
When the libraries have been successfully declared, the following screen appears:
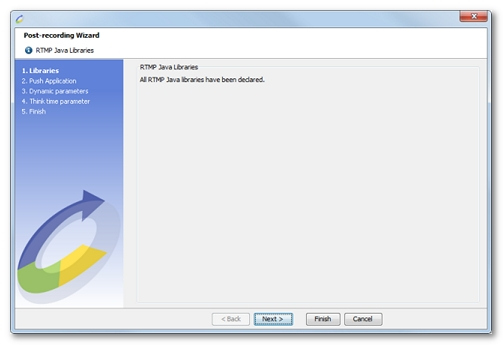
Declaring the Java RTMP libraries at the end of recording is a compulsory step if all the requests are to be played back.
-
You may declare missing Java RTMP libraries at a later stage.
-
Declaring Java RTMP libraries is carried out in the project's RTMP libraries manager in the project preferences. For more information, see Adobe RTMP.
RTMP requests with missing Java RTMP libraries are identified by a warning symbol:
NeoLoad then offers to create a modified User Path. This step is necessary because the User Path cannot be executed in its present state. For more details on the modifications NeoLoad automatically proposes, see RTMP streaming.
Record SSL-secure Adobe RTMPT requests
Note: This section only concerns the RTMPT protocol (RTMP encapsulated in the HTTP protocol).
The NeoLoad SSL certificate must be imported into the browser in order to record SSL-secure Adobe RTMP requests. The Adobe Flash plug-in checks the browser certificates and decides whether or not to authorize the Flash application to communicate with the server.
Importing the SSL certificate instructs the browser Adobe Flash plug-in to trust the NeoLoad recording proxy (Trusted).
For more information, see Record an HTTPS application.
Identifiers handled by NeoLoad
RTMP module automatically handles the following Adobe Flex/AMF identifiers:
-
clientId
-
messageId
-
DSId
-
responseURI
Note: The clientId and DSId can be handled manually by replacing their values with a variable.
With RTMPT, the session identifier used in the request path is handled by a Framework parameter.
SWF verification
SWF verification is a feature of RTMP servers that checks to make sure the connected client is the expected SWF file. Once the client is connected, the server sends a message to the client that must be answered with the correct signature. If the answer is invalid, the server refuses to communicate with the client.
Since NeoLoad passes itself off as a client during the scenario simulation, the server sends the verification message. However, the Adobe license that covers RTMP prohibits developing a client that can simulate this verification. NeoLoad therefore cannot send an answer to the server.
If, after recording, NeoLoad detects that SWF verification is enabled, the following message is displayed.
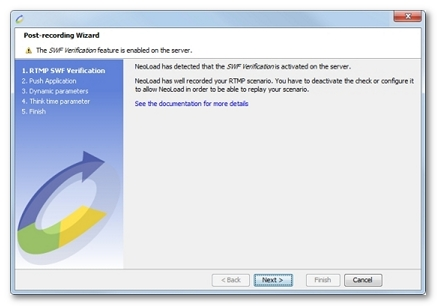
During runtime, if the server sends an SWF verification message, NeoLoad throws an NL-RTMP-PLUGIN-ENGINE-04 error. For NeoLoad to simulate this type of RTMP scenario correctly, SWF verification must be either disabled or configured to ignore verification for NeoLoad.
Disable SWF verification
To disable SWF verification, the application must be reconfigured. To do this, and if the configuration applies to all applications, the following file needs to be changed on the server: <Server>/conf/_defaultRoot_/_defaultVHost_/Application.xml; if the configuration applies to the specific application: <Server>/applications/<Application>/Application.xml.
Locate the following item in the configuration file:
<SWFVerification enabled="true">...</SWFVerification>
Replace enabled="true" with enabled="false" to disable SWF verification for all clients.
Ignore SWF verification for NeoLoad
To disable SWF verification for NeoLoad only, the application needs to be reconfigured. To do this, and if the configuration applies to all applications, the following file needs to be changed on the server: <Server>/conf/_defaultRoot_/_defaultVHost_/Application.xml; if the configuration applies to the specific application: <Server>/applications/<Application>/Application.xml.
Locate the following item in the configuration file:
<SWFVerification enabled="true">...</SWFVerification>Underneath this item, locate the <UserAgentExceptions> item and add the following entry immediately underneath it:
<Exception from="NeoLoad" to="NeoLoad" />The configuration should now look like this:
<SWFVerification enabled="true"> ... <UserAgentExceptions> ... <Exception from="NeoLoad" to="NeoLoad" /> </UserAgentExceptions> </SWFVerification>Finally, in NeoLoad, configure the request making the connection to tell the server that the client is NeoLoad. To do this, locate the "connect" request (the name may have the format "connect_X").
Then replace:
<flashVer tagClass="String">WIN 10,1,82,76</flashVer>with:
<flashVer tagClass="String">NeoLoad</flashVer>