Adobe Flex/AMF requests
Note: This feature uses Adobe Flex libraries, which NeoLoad no longer supports due to security concerns. If you wish to continue using this feature at your own discretion, please reach out to Tricentis support for help getting it back.
AMF is a binary, client-server data transfer protocol used by certain Adobe Flash applications. The optional AMF (Action Message Format) module allows load testing Adobe Flash applications developed using Adobe Flex technology, and using the AMF application protocol.
There are several variants of the AMF binary protocol:
-
AMF0: This version is used in Flex applications written in ActionScript 1.0 and 2.0.
-
AMF3: Adobe introduced this protocol, very similar to AMF0, from ActionScript 3.0 onwards. The protocol allows the exchange of objects created by the application developer between the client and server.
Note: Managing AMF requests requires the purchase of the optional Adobe FLEX/AMF XML module. This module is included in the demo version NeoLoad.
Dependent libraries
When recording AMF3 requests, depending on the server-side implementation, the Java classes of the objects exchanged have to be declared in NeoLoad. For more information, see Adobe Flex AMF.
Recording
The following diagram shows how the Adobe Flex/AMF module functions during the recording:
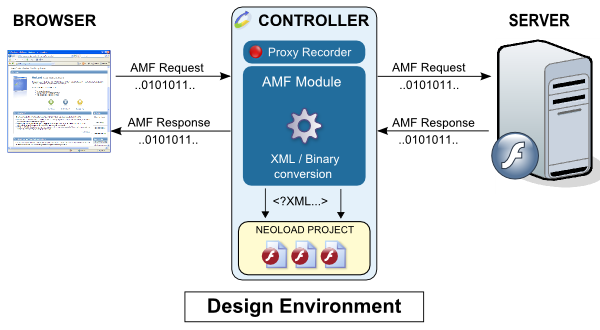
The binary data exchanged between the client and server transit through the recording proxy. It is during this transit that the Adobe Flex/AMF module analyzes and decodes the requests. Once they have been translated into XML, the requests are inserted in the project.
Execution
The following diagram shows how the Adobe Flex/AMF module functions when a test is run:
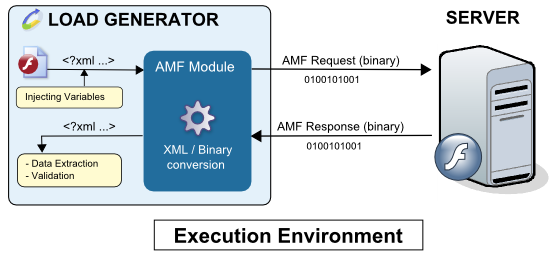
The variables in the XML request are calculated and the module engine translates the XML into binary data, which is then sent to the server. The binary response received is translated into XML, after which the validity checks and Variable Extractors in the played request are executed.
AMF streaming
In addition to the standard request/response exchange, the AMF protocol also can be used in streaming. In this case, the server is responsible for sending AMF packets to the connected client in real time.
NeoLoad handles Push technologies, including AMF streaming. For more information about the Push technologies supported by NeoLoad, see Push frameworks and Adobe Flex AMF. For more information about streaming, see Streaming requests.
Record SSL-secure Adobe Flex/AMF requests
To record SSL-secure Adobe Flex/AMF requests, the NeoLoad SSL certificate must be imported into the web browser. The Adobe Flash plug-in checks the browser certificates and decides whether or not to authorize the Flash application to communicate with the server.
Importing the SSL certificate tells the browser Adobe Flash plug-in that the NeoLoad recording proxy can be trusted.
For more information, see Record an HTTPS application.
Record requests with an Adobe AIR application
Introduction
Adobe AIR (Adobe Integrated Runtime) is a technology developed by the Adobe Corporation. NeoLoad supports Adobe AIR applications that communicate with the server using the HTTP protocol.
Prerequisites
The application must communicate with the remote server using the HTTP protocol.
Configure the recording and proxy settings
The following procedures describe how to configure the machine with or without Internet Explorer and how to record the HTTP requests sent by an Adobe AIR application.
To configure the proxy settings using Internet Explorer, follow these steps:
-
Open Internet Explorer.
-
Click Tools > Internet options.
-
Click on the Connections tab.
-
Click on the LAN settings button.
-
Check the Use a proxy server for your LAN. If proxy settings already exist, see Proxy.
-
Click on the Advanced button and set the proxy (localhost:
8090by default). For more information, see Manually configure the recording proxy settings.
The following procedure describes how to configure the proxy settings on a Windows machine that does not have Internet Explorer installed.
To configure the proxy settings without Internet Explorer, follow these steps:
-
Click on the Windows icon in the taskbar.
-
Click Control panel > Network and Internet Connections > Internet Options.
-
Click on the Connections tab.
-
Click on the LAN settings button.
-
Check the Use a proxy server for your LAN. If proxy settings already exist, see Proxy.
-
Click on the Advanced button and set the proxy (localhost: 8090 by default). For more information, see x.
Once the proxy settings have been configured correctly, continue as follows:
To record the Adobe AIR application HTTP requests once the proxy is configured, follow these steps:
-
Launch NeoLoad
-
Make sure the previously-configured proxy setting match those in Edit > Preferences > Global Settings > HTTP Recorder.
-
Create a new project or open an existing one.
-
Un-check the Launch browser check box, then click OK to start recording
-
Launch the Adobe AIR application and record the actions you require.
-
Stop the recording.
The recorded User Path contains the HTTP requests sent by the Adobe AIR application.
Note: The original proxy settings must be restored manually.
Post-recording wizard
At the end of recording, the JAR declaration panel is displayed if any Java classes or JAR files are missing:
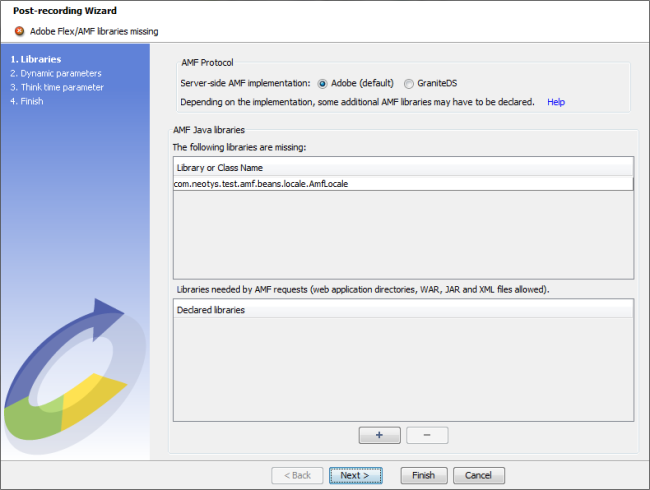
Depending on the server-side implementation of the Adobe Flex/AMF application being tested, it may be necessary to declare some AMF libraries to ensure the successful recording and playback of the AMF requests:
-
Externalizable objects (i.e. which implement
java.io.Externalizablein Java) are responsible for saving and restoring the contents of their instance. -
It is necessary to load all the classes of the externalized objects sent.
-
The panel lists some missing classes only: a few classes are unresolved.
To declare the missing AMF Java libraries (XML and JAR files), follow these steps:
-
Click the + button to open the file explorer.
-
Select an appropriate WAR file for the application, or the directory containing the deployed web application, then click Select. NeoLoad automatically retrieves the required JAR and XML files from the selected application. You also may select the JAR and XML files to be loaded manually in NeoLoad. Repeat the operation as many times as required.
A message confirms whether the declaration has been successful or not. Whenever an error occurs, make sure that all the necessary AMF Java libraries have been declared.
-
Once all the necessary libraries have been declared, the following screen is displayed:
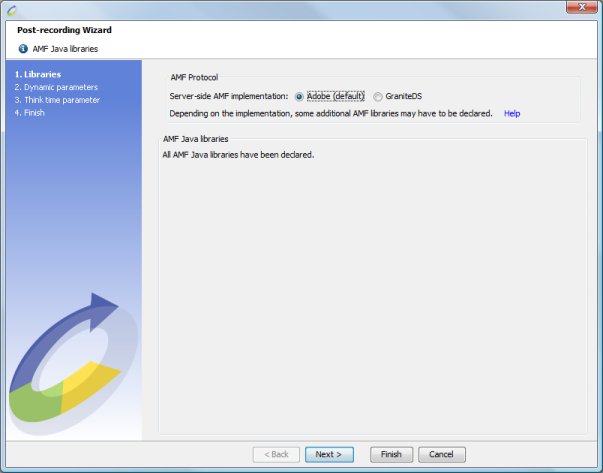
Declaring the AMF Java libraries at the end of the recording must be done to ensure successful playback of all the recorded requests.
-
The missing AMF Java libraries may be declared later.
-
Declaring AMF Java libraries is done in the project's AMF library manager, which can be accessed through the project preferences. For more information, see Adobe Flex/AMF.
AMF requests that are missing an AMF Java library are identified by a warning symbol:
Identifiers handled by NeoLoad
The Adobe Flex/AMF module automatically handles the following identifiers:
-
clientId -
messageId -
DSId -
responseURI
Note: You may handle the clientId and DSId manually by replacing their values with a variable.